Question
Question: In \[Ph-CH(OH)C{{H}_{3}}\xrightarrow{SOC{{l}_{2}}}Ph-CH(Cl)C{{H}_{3}}+S{{O}_{2}}+HCl\] Which of th...
In Ph−CH(OH)CH3SOCl2Ph−CH(Cl)CH3+SO2+HCl
Which of the following acts as a leaving group?
A. OH−
B. Cl−
C. SO2
D. 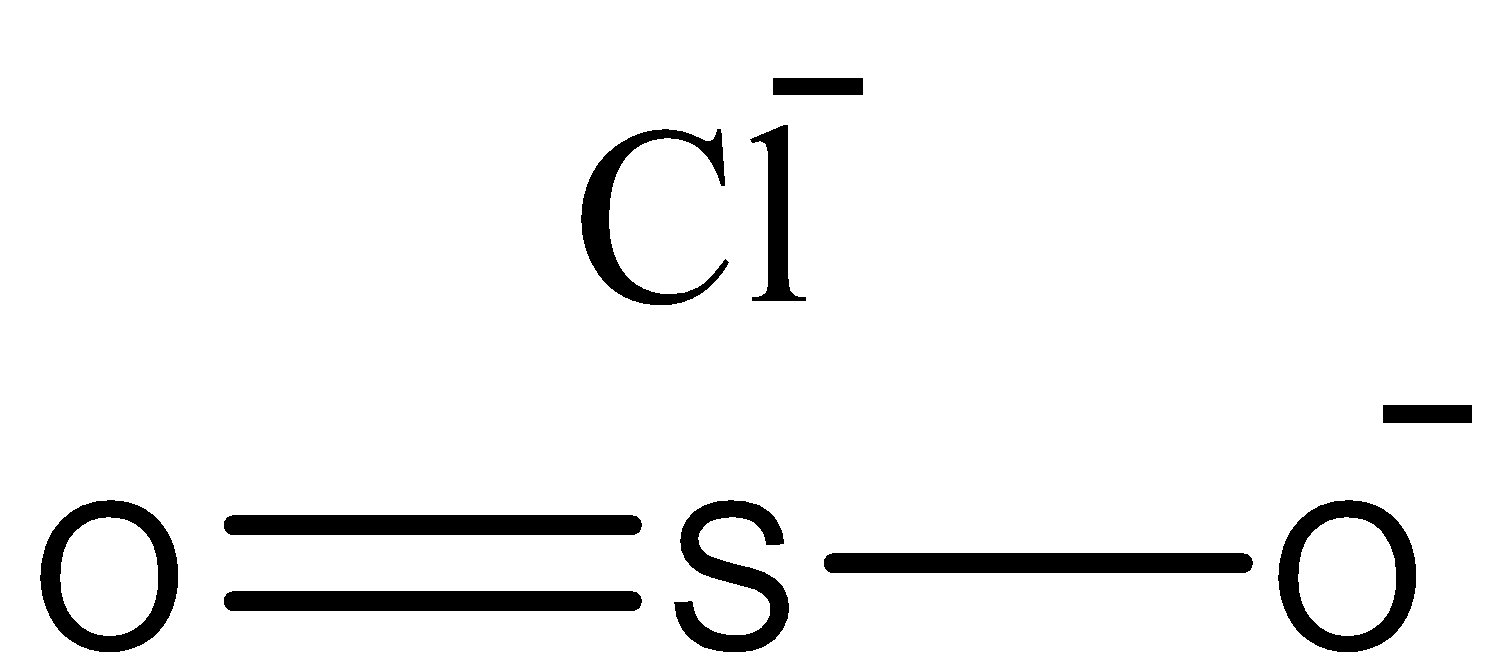
Explanation
Solution
Alcohols react with thionyl chloride and form their chloro derivatives (alkyl or aryl halides) as the products. This reaction is called chlorination. Chlorination is a best example for substitution reactions.
Complete step by step answer:
- In the given reaction aryl halide is reacting with thionyl chloride and forming its halide derivative and Sulphur dioxide and hydrochloric acid as by products.
Ph−CH(OH)CH3SOCl2Ph−CH(Cl)CH3+SO2+HCl
- In the question it mentioned that we have found the leaving group in the reaction.
- To know about the leaving group we should write the mechanism of the given reaction.
The mechanism of the given reaction is as follows.
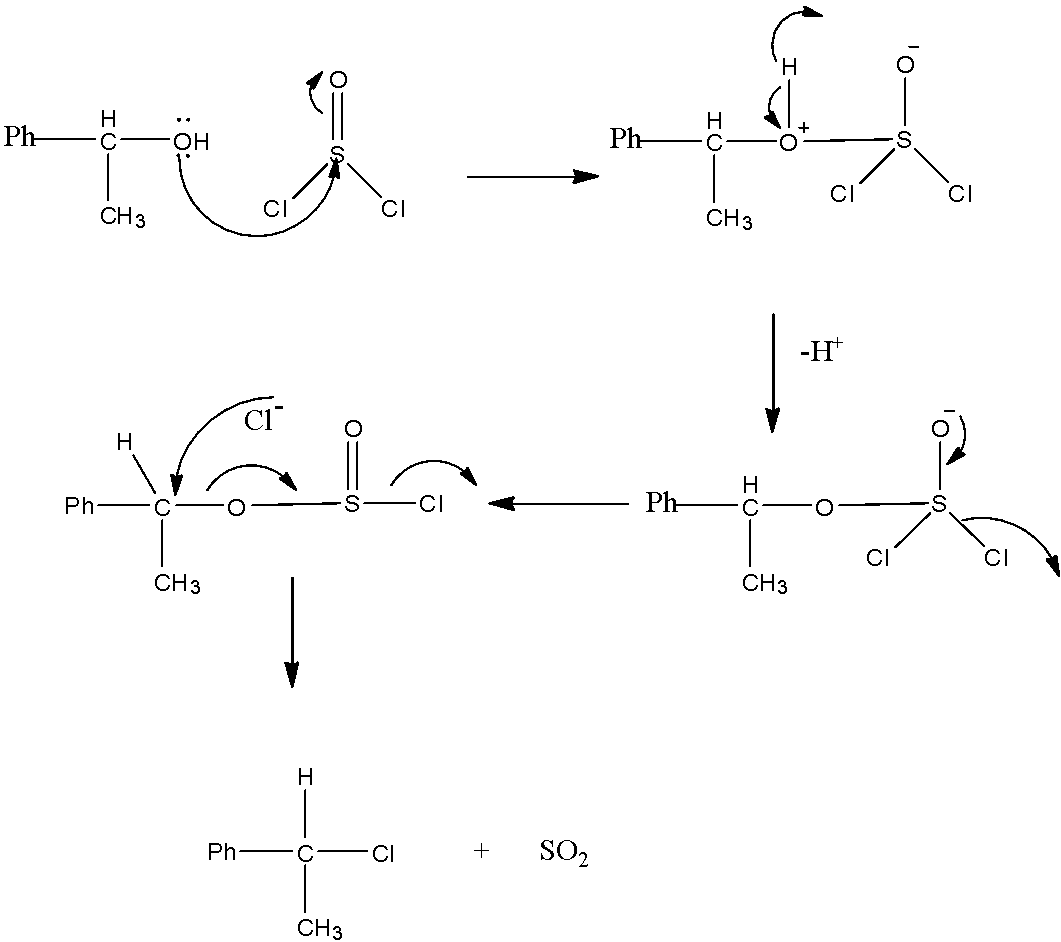
- In the first step, a lone pair of electrons on oxygen on alcohol attacks on the electron deficient Sulphur atom.
- Later to stabilize the hydrogen atom of alcohol comes out as a hydrogen ion, in continuation the negative charge on the oxygen attached to Sulphur is getting stabilized by donating electrons to Sulphur in the process chloride ion comes out.
- The liberated chloride ion attacks on the carbon which is attached to Sulphur through oxygen.
- At that time in the process of stabilization Sulphur dioxide was liberated as a by-product.
- In the given reaction the liberated product is Sulphur dioxide.
So, the correct option is C.
Note: All of us think that in the given reaction the hydroxyl group is converting into halogen in the product. So, the liberated product is the hydroxide group (OH−). But through mechanism only we can say which group is going to substitute in the reaction.
