Question
Question: In Oppanauer's oxidation: (A) Secondary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid in acetone solvent ...
In Oppanauer's oxidation:
(A) Secondary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid in acetone solvent using aluminium tertiary butoxide.
(B) Secondary alcohol is oxidized to carboxylic acid without affecting the C=C or C≡C bond by aluminium tertiary butoxide in acetone solvent.
(C) Secondary alcohol is oxidized to ketone without affecting the C=C or C≡C bond by aluminium isopropoxide.
(D) Secondary alcohol is oxidized to ketone by chromic acid-pyridine complex.
Solution
To solve this question, we must first understand the concept of Oppanauer's oxidation. Then we need to assess the important points of the concept in order to select the most appropriate option and then only we can conclude the correct answer.
Complete step-by-step answer: Before we move forward with the solution of this given question, let us first understand some basic concepts:
Oppanauer's oxidation:
Oppenauer oxidation is a gentle method for selectively oxidizing secondary alcohols to ketones. The alcohol is oxidized with aluminium isopropoxide in excess acetone. This shifts the equilibrium toward the product side.
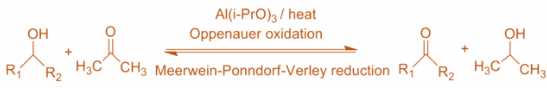
The oxidation is highly selective for secondary alcohols and does not oxidize other sensitive functional groups such as amines and sulfides. Though primary alcohols can be oxidized under Oppenauer conditions, primary alcohols are seldom oxidized by this method due to the competing aldol condensation of aldehyde products.
The Oppenauer oxidation is still used for the oxidation of acid labile substrates. The Oppenauer oxidation is commonly used in various industrial processes such as the synthesis of steroids, hormones, alkaloids, terpenes, etc.
So, after going through the reaction and also the above statements we can conclude that in Oppanauer's oxidation Secondary alcohol is oxidized to ketone without affecting the C=C or C≡C bond by aluminium isopropoxide.
So, clearly we can conclude that the correct answer is Option (C).
Note: Oxygen and atmospheric moisture are the major players in corrosion and oxidation. It is a metal surface’s chemical reaction with oxygen that causes some metal to corrode and form the surface’s oxidation or better known as metal oxide.
