Question
Question: In mammals, the organ of Corti is found in (a) Scala vestibuli (b) Scala tympani (c) Scala med...
In mammals, the organ of Corti is found in
(a) Scala vestibuli
(b) Scala tympani
(c) Scala media
(d) Cochlear canal
Solution
The organ of Corti which is also called a spiral organ, is the receptor organ for hearing and is found within the mammalian cochlea. This is a highly varied strip of epithelial cells that allows for the transduction of auditory signals into nerve impulses.
Complete answer:
The organ of Corti is an organ of the internal ear contained within the scala media of the cochlea. It resides on the membrane, a stiff membrane separating the scala tympani and scala media. The scala media may be a cavity within the cochlea that contains endolymph which features a high K+ concentration. The endolymph helps to manage the electrochemical impulses of the auditory hair cells.
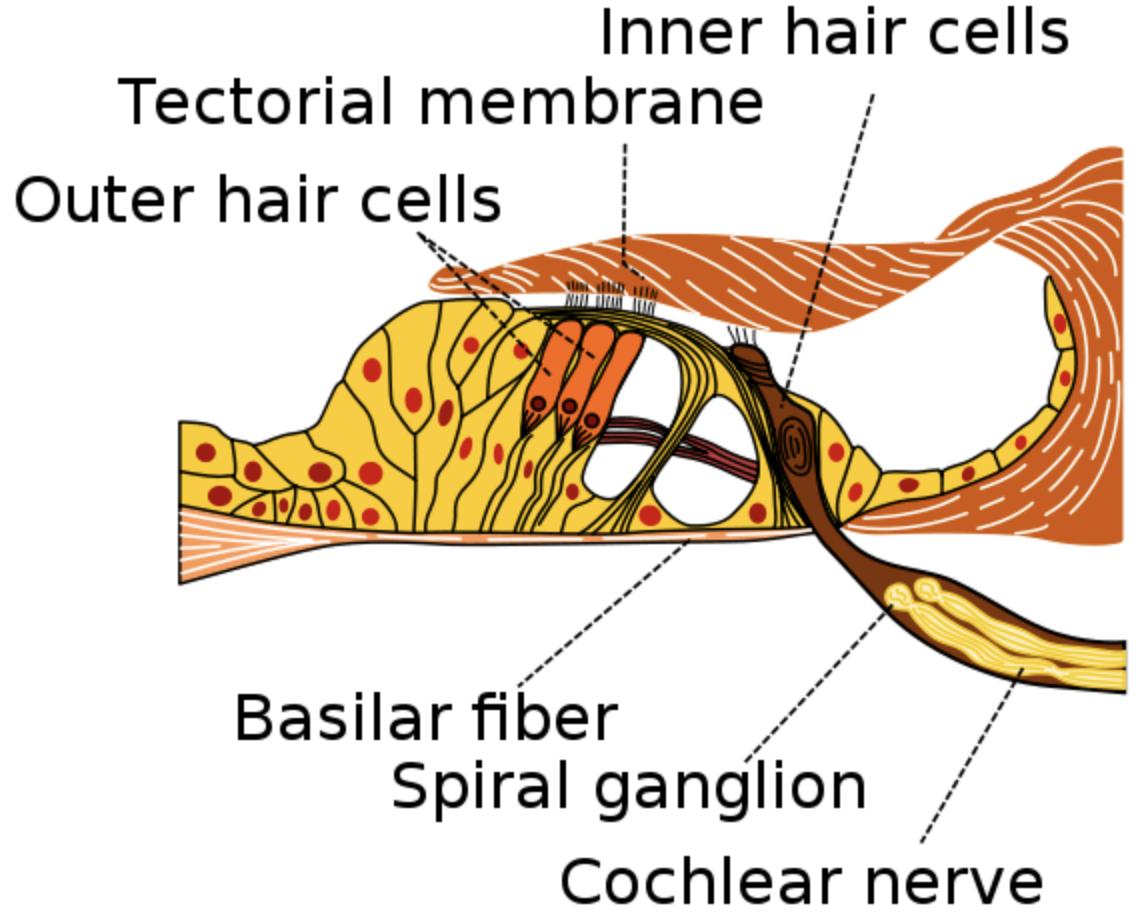
The first function of the organ of Corti is the transduction of auditory signals. The organ of Corti consists of both supporting cells and mechanosensory hair cells. The arrangement of mechanosensory cells is into inner and outer hair cells along rows. The supporting cells also are named Dieters or phalangeal cells.
Inner hair cells function primarily because of the sensory organs for an audition. they supply input to 95% of the acoustic nerve fibers that project to the brain
The hair cells within the organ of Corti have stereocilia that attach to the tectorial membrane. Shifts between the tectorial and basilar membranes move these stereocilia and activate or deactivate receptors on the epithelial cell surface.
Additional Information:
- Sound waves enter the ear via the auditory meatus and cause a vibration of the eardrum. Movement of the eardrum causes subsequent vibrations within the ossicles, the three bones of the center ear which transfer the energy to the cochlea through the fenestra ovalis.
- As the fenestra ovalis moves, waves transfer to the perilymph fluid inside the scala tympani then the scala vestibuli of the cochlea. When fluid moves through these structures, the membrane (located between the scala media and scala tympani) shifts respectively to the tectorial membrane.
- The artery of the labyrinth is the main supplier of oxygenated blood to the cochlea and thus the organ of Corti. This artery is additionally referred to as the auditory artery or internal auditory artery. The artery of the labyrinth most ordinarily originates from the anterior inferior arteria cerebelli (AICA).
So the correct answer is ‘Scala media’.
Note:
- Electrode array placement into the cochlea may be a current treatment option for high- grade sensorineural deafness. Surgical complications are typically related to surgical technique or device failure. Complications classify as either minor or major.
- The commonest minor complication includes infections, vestibular problems, and tinnitus formation. Major complications include more serious infections, damage to middle or internal ear structures, and device failure problems.
- Sensorineural deafness is the most ordinarily reported explanation for auditory deficits. This sort of deafness often results from exposure to either loud sounds or ototoxic drugs. Exposure to loud noises causes the vibrational shift between the tectorial and basilar membranes to extend.
