Question
Question: In homogeneous catalytic reactions, there are three alternative paths A, B and C (shown in the figur...
In homogeneous catalytic reactions, there are three alternative paths A, B and C (shown in the figure). Which one of the following indicates the relative ease with which the reaction can take place?
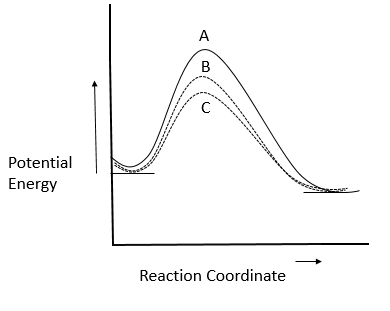
A. A > B> C
B. C > B> A
C. B > C> A
D. A = B = C
Solution
If a chemical reaction reactants and catalyst are within the same phase that’s liquid or gaseous phase, then the catalyst may be a homogeneous catalyst. If the reactants and catalyst are in different phases, then the catalyst may be a heterogeneous catalyst.
Complete step by step answer:
We must remember that the catalyst is defined as a substance which accelerates the rate of reaction and themselves remain chemically and quantitatively unchanged after the reaction.
Now we can discuss the types of catalysts. There are two types of catalysts which are,
Homogeneous and heterogeneous catalyst.
Homogeneous catalyst: A catalyst which exists within the same phase as that of reactants is known as a homogeneous catalyst. Catalyst and reactants sort a single phase. The catalyst dissolves within the gas phase or solution.
Catalyst can’t be easily separated from the products of the reaction. The rate of reaction independent of surface area of the catalyst.
Activation energy within the different paths lies in the following sequence:
Lesser is that the energy of activation, greater is that the ease with which the reaction can take place. C >B > A.
Decreasing ease with which the reaction takes place.
So, the correct answer is Option B.
Note: We also remember that the reactions which involve homogeneous catalysts are faster than the one involving heterogeneous catalysts. Homogeneous catalyst is employed in hydrolysis of sugar and esters. Heterogeneous catalyst is used in manufacturing ammonia, Ostwald’s process and hydrogenation of vegetables oils to ghee.
