Question
Question: In glycolysis, during oxidation, electrons are removed by - (a)ATP (b)Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate...
In glycolysis, during oxidation, electrons are removed by -
(a)ATP
(b)Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate
(c)NAD+
(d)Molecular oxygen
Solution
The process of glycolysis occurs in every living cell of the body. It occurs in ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. During oxidizing reaction, an oxidizing agent accepts electrons and reduces itself in the step catalyzed by glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Complete answer:
- Glycolysis is the first step in respiration of living cells. It is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose to pyruvate through ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions.
- In the oxidation reaction, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate is oxidized, resulting in the removal of a pair of electrons by NAD+ and the addition of a phosphate group to form 1,3-diphosphoglyceric acid.
- NAD+ is thus an oxidizing agent which reduces itself by accepting electrons and forming NADH.
- The reaction is given as NAD++Pi⟶Glyceraldehyde3−phosphatedehydrogenaseNADH+H+. As denoted, the reaction is catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Additional Information:
- In glycolysis, one molecule of glucose produces four ATP, two NADH, and two pyruvate molecules.
- Although four ATP molecules are formed, two molecules of ATP are already used in the first half of glycolysis, thus the net gain is two ATP molecules.
- The two pyruvate molecules formed are further used in starting the Krebs/Citric acid cycle.
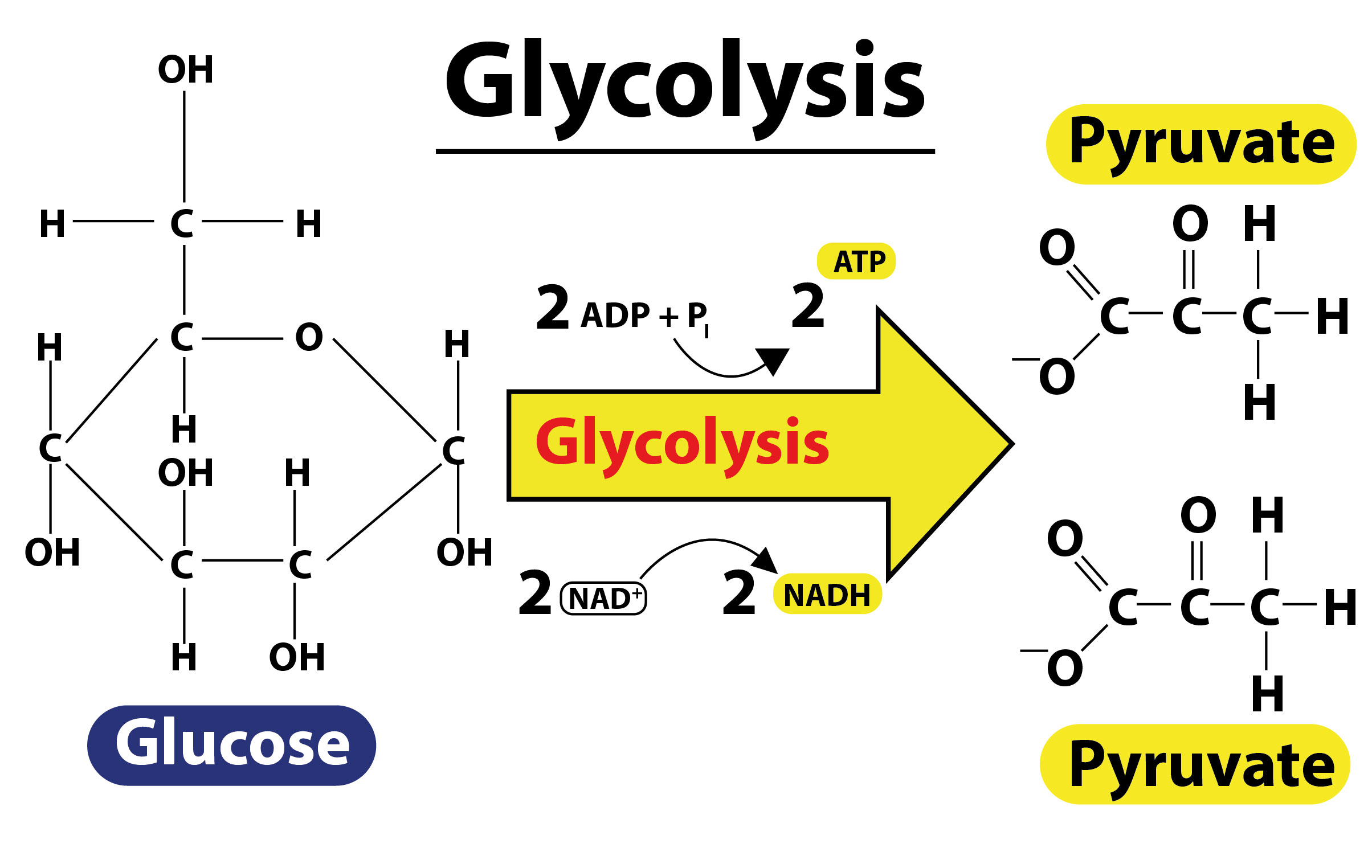
So, the correct answer is ‘NAD+’.
Note: - Red blood cells, or erythrocytes, are solely reliant on glycolysis as a source of energy because they do not have mitochondria.
- The enzymes involved in glycolysis are rate limiting steps and are needed in sufficient quantities for the reactions to continue.
