Question
Question: In fructofuranose, OH group of which carbon adds to \( > C = O\) group? A. \({C_3}\) B. \({C_4}\...
In fructofuranose, OH group of which carbon adds to >C=O group?
A. C3
B. C4
C. C5
D. C3
Solution
As we know five- and six-member rings are the most common structures of cyclic monosaccharide. Cyclic monosaccharides with five-member rings are known as furanoses, and those that contain six member rings are known as pyranoses. We could draw the open chain structure of fructofuranose, and mark the OH group on carbon that adds to C=O group.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to know that pyranoses and furanoses, the aldehydic (or) ketonyl carbon turns into new asymmetric carbon. The furanoses contain a hydroxyl group called anomeric hydroxyl group. The spatial arrangement of hydrogen and hydroxyl groups around the new asymmetric carbon leads to anomerism, an additional stereoisomerism, and the carbon is called anomeric carbon.
An equilibrium mixture of α and β anomers exist by each pyranose (or) furanose. This is based on the spatial arrangements of hydrogen and hydroxyl groups on the anomeric carbon.
We have to know that in α anomers like α-D-glucopyranose and α-D-fructofuranose, the hydroxyl group of anomeric carbon is oriented furthest from CH2OH group present at the other end of the molecule.
We have to know that in β anomers like β-D-glucopyranose and β-D-fructofuranose, the anomeric hydroxyl group is kept close to that CH2OH group.
In a solution, each pyranose (or) furanose isomer is found as an equilibrium mixture of its α and β anomers.
We can draw the open chain structures of β-D-fructofuranose as,
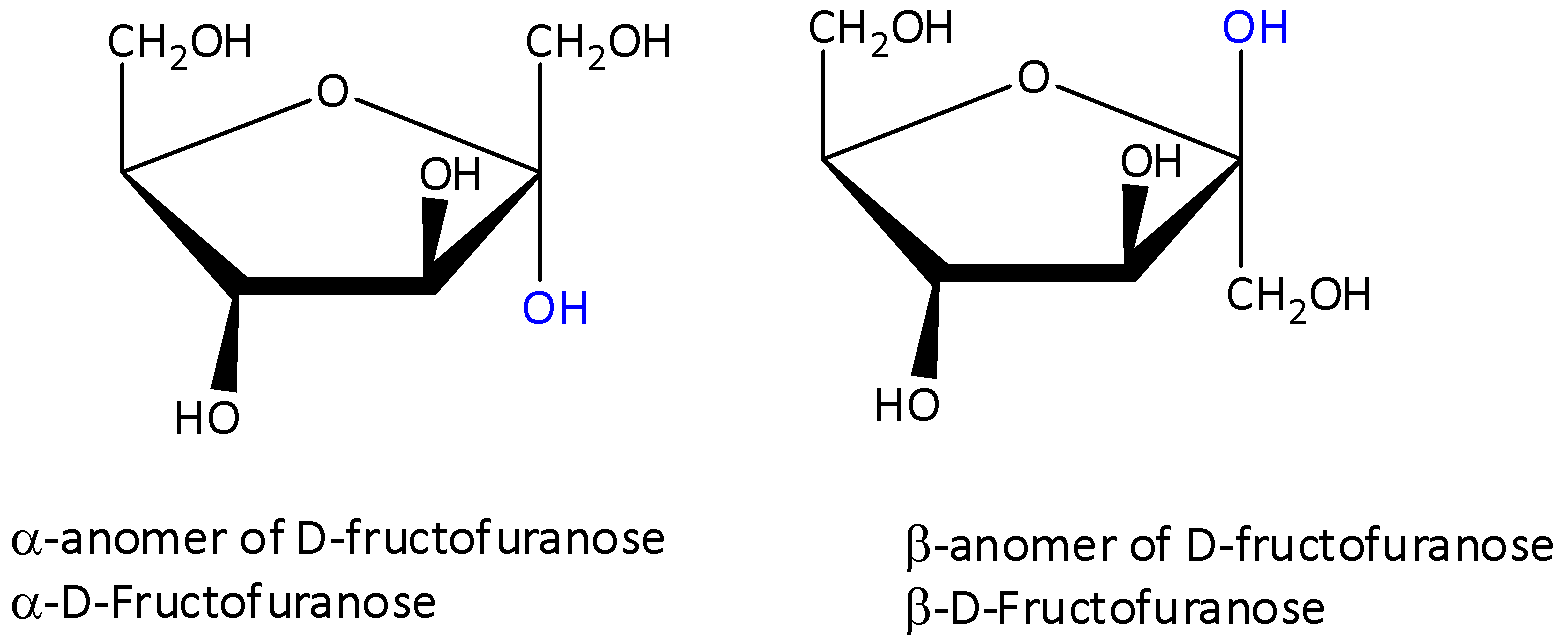
In the open chain structure fructofuranose drawn above, we can see that the marked hydroxyl group that adds to C=O is on C5 carbon.
So, the correct answer is Option C.
Note:
We know that Sucrose is otherwise called common table sugar. It is a disaccharide of α-d-glucopyranose and β -d-fructofuranose in which the anomeric centers are linked. Both ketal and acetal functional groups are present in sucrose.
