Question
Question: In figure, XY and X'Y' are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB wi...
In figure, XY and X'Y' are two parallel tangents to a circle with centre O and another tangent AB with point of contact C intersecting XY at A and X'Y' at B. Prove that
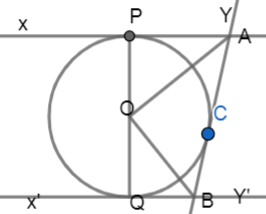
Solution
Hint: In this question, we need to draw the diagram clearly in order to understand the relation between the angles. We need to use the similarity property and the properties of two parallel lines with a transversal.
Complete step-by-step Solution:
Let us look at some of the basic definitions.
CIRCLE: Circle is defined as the locus of a point which moves in a plane such that its distance from a fixed point in that plane is constant.
TANGENT: In geometry, a tangent line to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point, never entering the circle's interior
CONGRUENCE OF TRIANGLES:
Two triangles that are identical in all respects are said to be congruent and are denoted by the symbol ≅. In two congruent triangles,
The corresponding sides are equal.
The corresponding angles are equal.
Conditions for two triangles to be congruent:
Three sides of one triangle are respectively equal to three sides of the second triangle (SSS).
Two sides and the included angle of one triangle respectively equal to two sides and the included angle of another triangle (SAS).
Two angles and the included side of one triangle are respectively equal to two angles and the included side of another triangle (ASA).
Two right angled triangles are congruent, if the hypotenuse and one side of one triangle are respectively equal to the hypotenuse and one side of another right angled triangle (RHS).
Now, let us look at the diagram clearly,
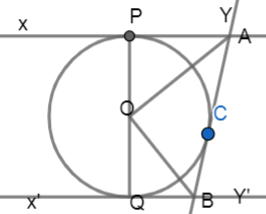
As we already know that tangent to a circle is perpendicular to the radius of circle at the point of contact.
OP⊥XY
OC⊥AB
In triangle OPA and OCA
∠OPA=∠OCA=90∘
As they are tangents to the circle at points P and C.
OP=OC
As they are radii of the same circle.
AP=AC
We already know that lengths of the tangent from an external point are equal.
Now, by observing the above conditions from SAS congruence we can say that,
∴△OPA≅△OCA
∴∠OAP=∠OAC
∴∠OAC=21∠PAC
Similarly, we can also say that.
