Question
Question: In expiration condition, the diaphragm becomes A. Circular B. Relaxed C. Fully contracted D...
In expiration condition, the diaphragm becomes
A. Circular
B. Relaxed
C. Fully contracted
D. Expanded
Solution
Respiration is defined as the exchange of environmental oxygen with the carbon dioxide produced in the cells during oxidation at a moist surface. It is a complex process during which digested food is oxidized to release chemical energy.
Complete step-by-step answer:
1. Respiration is a biochemical process that takes place inside the cell. It involves a series of reactions, all of them catalyzed by a specific enzyme. Respiration occurs in two phases: i)Breathing or external respiration ii) Internal or tissue respiration.
2. Expiration: it is normally a passive process as it simply involves relaxation of the inspiratory muscles, viz., peripheral muscles of the diaphragm, and external intercostals muscles.
3. The peripheral muscle of the diaphragm relaxes. With this, the abdominal viscera compressed during inspiration, pushes the diaphragm upward, making it convex.
4. External intercostals muscles also relax. This brings the ribs and the sternum to their original position. This is aided by the elastic recoil (contraction) of the lungs and thoracic wall which are stretched during inspiration.
4. Inspiration: it is an active process. It is brought about by diaphragm muscles and external intercostals muscles. These muscles are called inspiratory muscles.
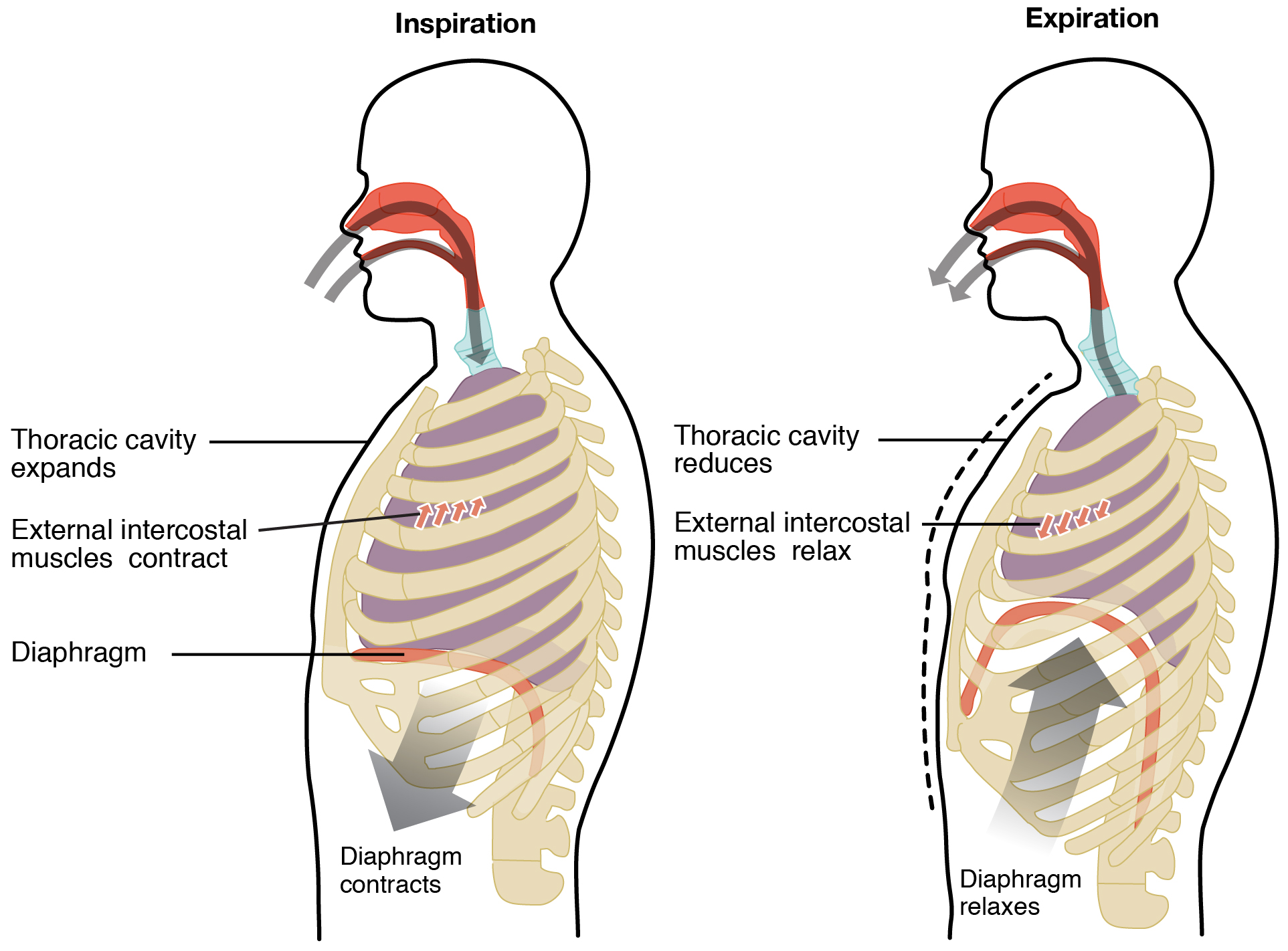
So, the correct answer is “Option B Relaxed”.
Additional information:
The diaphragm is convex upward and has a peripheral muscle attached to the ribs and vertebral column. This muscle contracts and lowers the diaphragm, making it flat. This pushes the abdominal viscera downward and enlarges the thoracic cavity vertically.
Note: Lungs can be expanded or contracted in two ways: by downward and upward movement of the diaphragm to expand or contract the chest cavity and by raising or lowering of the ribs to increase or decrease the diameter of the chest cavity.
