Question
Question: In \({E_2}\) elimination some compounds follows Hoffmann's rule which means : A. The double bond g...
In E2 elimination some compounds follows Hoffmann's rule which means :
A. The double bond goes to the most substituted position
B. The compound is resistant to elimination
C. No double bond is formed
D. The double bond goes mainly towards the least substituted carbon
Solution
We know that most of the compounds obey Zaitsev's rule, some give products according to Hofmann rule. Hofmann elimination is determined for compounds consisting of bulky leaving groups like quaternary ammonium or sulfonium salts.
Complete step by step answer:
We know that E2 represents bimolecular elimination. The reaction includes a one-step mechanism where carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bonds break to form a double bond.
Some of the important features of E2 eliminations are,
1.Two groups leave together.
2.Involves one step i.e. no intermediates formation takes place.
3.Both substrates and nucleophiles take part in a single step that is bimolecular reaction.
4.The base abstracts the beta-hydrogen and leaving group jointly leaves such that it results in the formation of a multiple bond between alpha and beta carbon atoms
5.The rate of the reaction is second order, as it is influenced by the alkyl halide as well as the base.
6.A strong base is used by E2 elimination and it should be strong to remove the acidic hydrogen that is weak.
We have to lower the hybridization of carbon from sp3 to sp2 for the creation of pi bonds.
E2 eliminations are also possible for central secondary alkyl halides and other compounds, though primary alkyl halides are the typical reactants/substrates that undergo E2 eliminations.
Hofmann eliminations are the elimination reaction of quaternary ammonium salts. The ability of Hofmann eliminations to form the less-substituted double bond isomer is generally called the Hofmann Rule.
In E2 elimination certain compounds obeys Hoffmann's rule. This describes that the double bond majorly goes in the direction of the least substituted carbon
When we heat 2-fluorobutane with potassium hydroxide, 1-butene and 2-butene are formed. In this reaction, the major product is 1-butene.
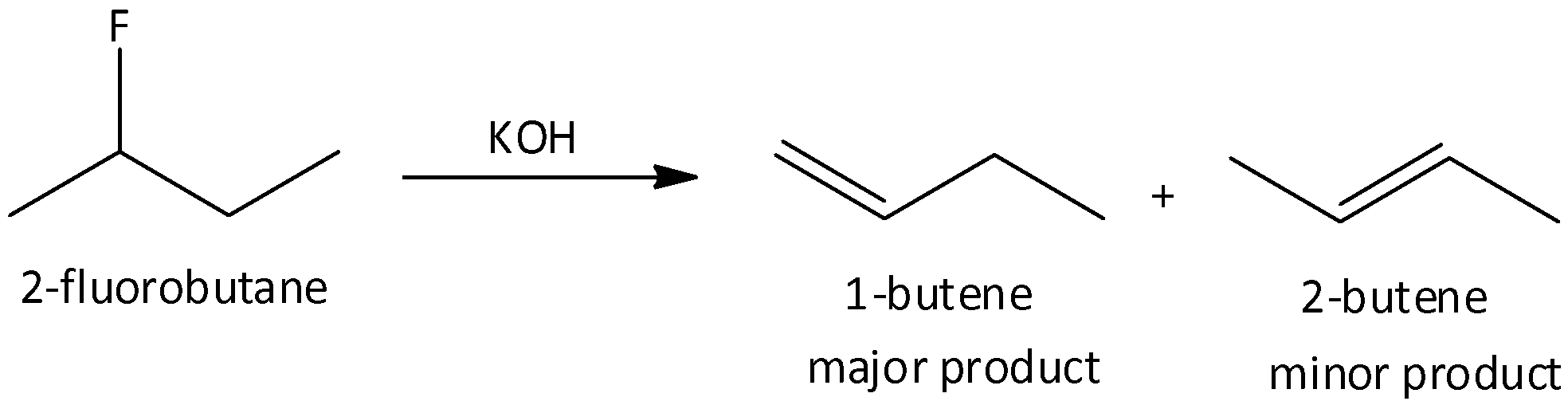
So, the correct answer is Option D.
Note:
We have to know that E2 elimination competes with SN2 reactions. This is because of the inherent tendency of the incoming nucleophile to attack the carbon atom containing the leaving group. Such situations would result in substitution products. We know that Zaitsev’s rule states that in an elimination reaction, the major product produced would be a more substituted alkene. This means that removal of the hydrogen form the more substituted beta-carbon atom must take place.
