Question
Question: In DNA, the complementary bases are: A.Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine B.Adenine and th...
In DNA, the complementary bases are:
A.Uracil and adenine; cytosine and guanine
B.Adenine and thymine; guanine and cytosine
C.Adenine and thymine; guanine and uracil
D.Adenine and guanine; thymine and cytosine
Solution
The macromolecule of DNA is made up of two complementary strands that form individual sub - units known as nucleotides. These bonds are responsible for the formation of complementary base sequences of nitrogenous bases that participate in the holding together of two DNA strands that form the double helical structure.
Complete Step-by-Step Answer:
Before we move forward with the solution of the given question, let us first understand some important basic concepts.
DNA is the short for Deoxyribonucleic Acid. This compound contains all the genetic data of an organism. This compound is made up of several smaller constituent compounds
These nucleotides are further made up of three different parts, viz. a phosphate group, a deoxyribose sugar and a nitrogenous base.
Now these nitrogenous bases are further classified into 4 types. The nucleotide molecules contain only one of these nitrogenous bases. The names of these nitrogenous bases are adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), and thymine (T). Two of the nucleotides so formed are bonded and held together by hydrogen bonds that take place between the nitrogenous bases. But there are certain conditions that must be followed while bonding of these nitrogenous bases take place. Adenine forms bonds only with thymine while guanine forms bonds with only cytosine.
Hence, Option B is the correct option
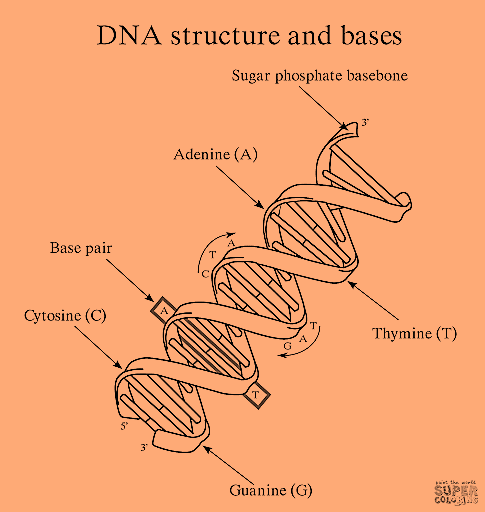
Note: These nucleotides come together to form long chains known as DNA strands. Two complementary DNA strands bond to each other in what looks like a ladder before winding into the double helix form.
