Question
Question: In \[\Delta ABC\], circumradius is 3 and inradius is 1.5 units, then the value of \[a{\cot ^2}\left(...
In ΔABC, circumradius is 3 and inradius is 1.5 units, then the value of acot2(A)+b2cot3(B)+c3cot4(C)is
A. 53
B. 73
C. 133
D. None of these
Solution
First of all, find the ratio of the circumradius and inradius of the given triangle to know whether it is an equilateral triangle or not. If it is an equilateral triangle then all the angles in the triangle are equal and thus the sides. So, use this concept to reach the solution of the given problem.
Complete step by step answer:
Given circumradius of ΔABC is R=3
Inradius of ΔABC is r=1.5
Now consider the ratio of circumradius and inradius i.e., R:r=3:1.5=2:1
We know that if the ratio of circumradius and inradius of a triangle is 2:1, then the triangle is an equilateral triangle.
So, ΔABC is an equilateral triangle i.e., all the three angles are equal to 600 as shown in the below figure.
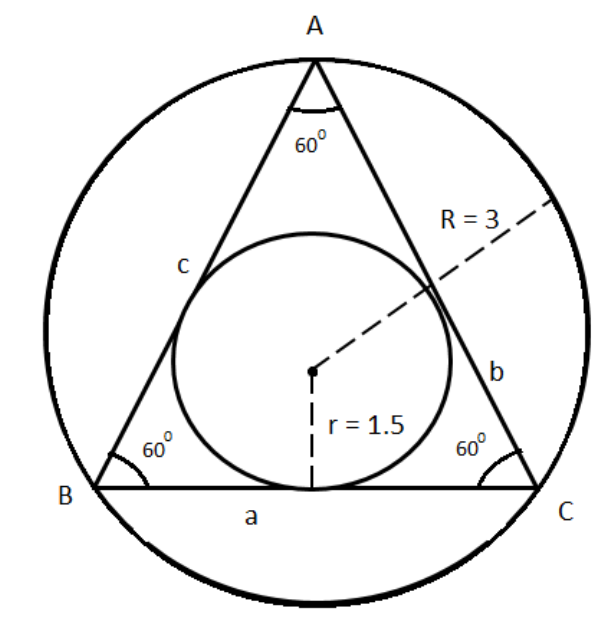
As ΔABC is an equilateral triangle it must satisfy that a=b=c=2Rsin3π=R3
Now, consider acot2(A)+b2cot3(B)+c3cot4(C)
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: If the ratio of circumradius and inradius of a triangle is equal to 2:1, then that triangle is an equilateral triangle in which all the sides and the angle are equal. Circumradius is defined as the radius of that circle which circumscribes the triangle and the inradius is defined as the radius of the circle which is inscribed in the triangle.
