Question
Question: In dehydrohalogenation of ethyl chloride, which of the following changes occurs? A.\(s{p^2}\)carbo...
In dehydrohalogenation of ethyl chloride, which of the following changes occurs?
A.sp2carbon converts to sp3 carbon
B. sp2carbon converts to sp carbon
C. sp3carbon converts to sp carbon
D. sp3carbon converts to sp2 carbon
Solution
Dehydrohalogenation reaction is a reaction in which a hydrogen halide got removed from a substrate in presence of alcoholic potassium hydroxide.
Complete step by step answer:
First, we have to discuss the structure of ethyl chloride. When one hydrogen of an ethene molecule is replaced by a chlorine atom, ethyl chloride forms.
CH3−CH2Cl
Now, we understand about the reaction of ethyl chloride with potassium hydroxide. When ethyl chloride reacts with potassium hydroxide both nucleophilic substitution and elimination reaction takes place.
Now, we discuss the elimination reaction of ethyl chloride. In ethyl chloride, βhydrogens present.
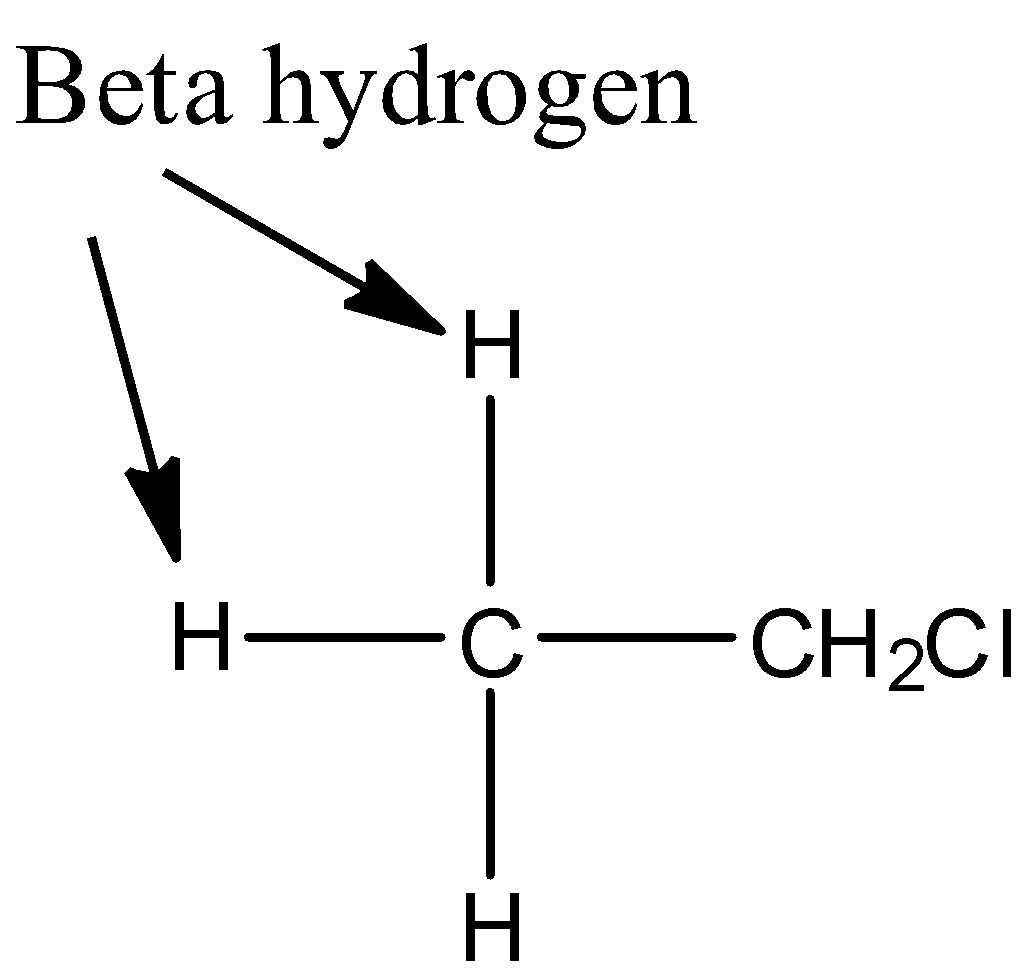
Due to which, it undergoes elimination reaction to produce ethene in presence of strong base like potassium hydroxide.
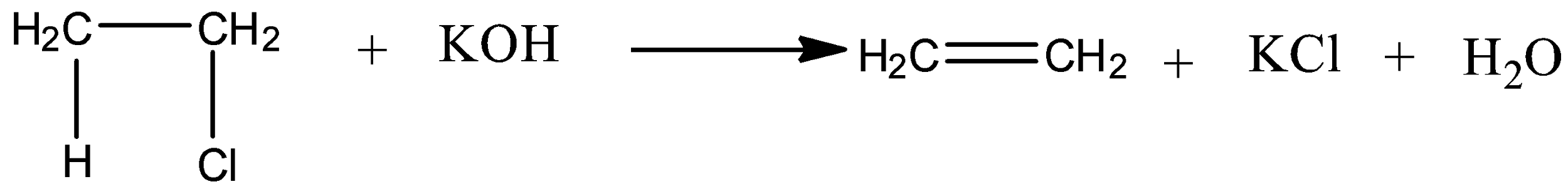
Now, let's discuss the mechanism of dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl chloride.
As ethyl chloride is a primary halide, E2 reaction is preferred over E1. E2 reaction is a one step reaction in which a carbon-hydrogen and carbon-halogen bond breaks simultaneously.
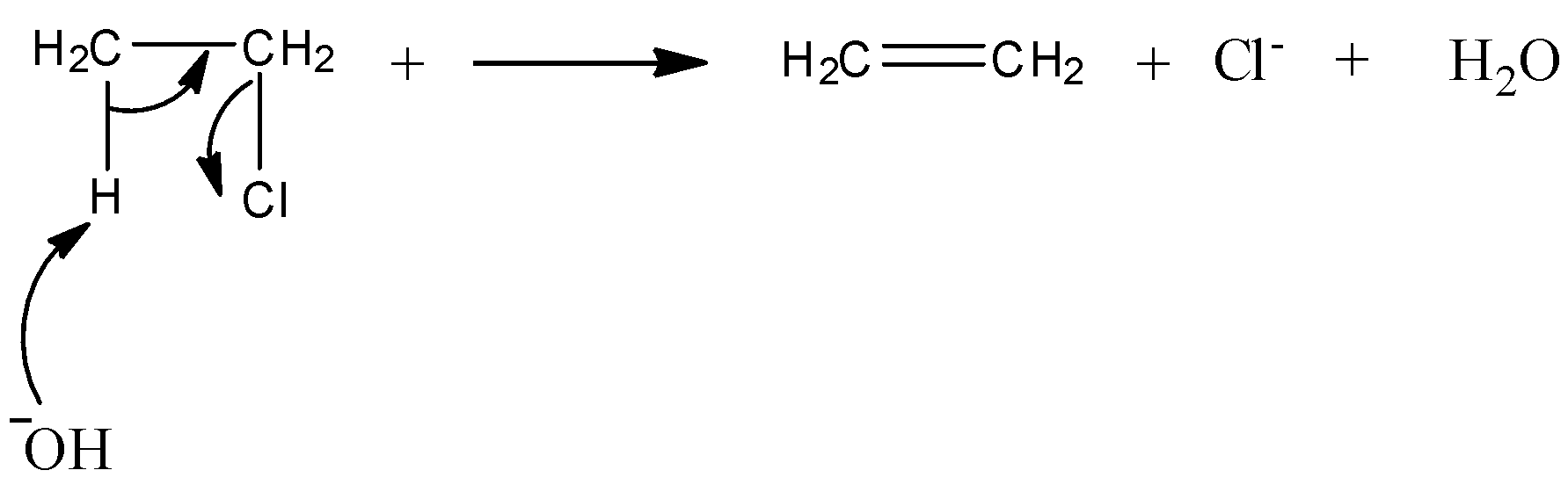
From the above mechanism, we get to know that ethene is formed on reaction of ethyl chloride with potassium hydroxide.
Now, we have to decide the type of carbon in the reactant and product. As the reactant contains only single bonds, so, the type of carbon is ethyl chloride is sp3. The product of dehydrohalogenation reaction of ethyl chloride is ethene which contains double bond, so, the type of carbon is ethene is sp2. So, the type of carbon in the product is sp2, that means, on dehydrohalogenation, sp3carbon converts to sp2 carbon.
Hence, the correct option is D.
Note:
Ethyl chloride also undergoes nucleophilic substitution on reaction with potassium hydroxide. The nucleophilic substitution reaction results in ethanol and potassium chloride.
C2H5Cl+KOH(aq)→C2H5OH+KCl
