Question
Question: In case of incomplete dominance, F2 generation has A. Genotypic ratio equal to phenotypic ratio ...
In case of incomplete dominance, F2 generation has
A. Genotypic ratio equal to phenotypic ratio
B. Genotypic ratio is 3:1
C. Phenotypic ratio is 3:1
D. None of the above
Solution
Incomplete dominance results in a third phenotype in which the expressed physical characteristic is the combination of the recessive and dominant phenotypes.
Complete answer:
Incomplete dominance is a process of gene interaction, which partially expresses both alleles of a locus gene, often leading to an intermediate or different phenotype. It is also called partial dominance. Incomplete dominance is that none of the two alleles dominates the other. This contributes to the combination of a phenotype. Experiments on pea plants were performed by Gregor Mendel. He studied seven characters with different characteristics and they all displayed the same heritage pattern. He generalized the rule of inheritance on this basis. Later, Mendel's work on other plants was replicated by researchers. They were surprisingly aware of the difference of the F1 Generation from the normal heritage pattern. The monohybrid cross led to F1 progeny, not an intermediate progeny but a parent-like parent.
Incomplete dominance is one type of intermediate inheritance in which one allele for a particular characteristic is not expressed entirely over its paired allele. This results in a third phenotype in which the expressed physical characteristic is the combination of the recessive and dominant phenotypes. The studies of cross pollination between red and white snapdragon plants show incomplete dominance. The allele producing red (RR) colour is not fully expressed over the recessive allele producing white (rr) colour. The resulting all offsprings are pink (Rr). When the F1 was self-pollinated the F2 resulted in the same genotypic and phenotypic ratio which is 1 (RR): 2 (Rr): 1 (rr).
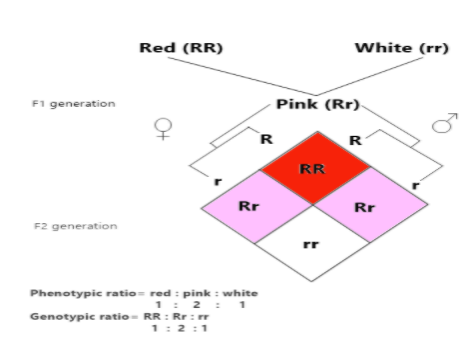
Thus, the correct answer is option ‘A’. i.e., Genotypic ratio equal to phenotypic ratio.
Note: Incomplete dominance means that a dominant allele or shape of a gene does not mask entirely the effects of a recessive allele and the resulting physical appearance of the organism shows a mixture of both alleles. It is often referred to as partial or semi-dominance.
