Question
Question: In benzene, what is the hybridization on each carbon atom? A)\({\text{s}}{{\text{p}}^2}\) B)\({...
In benzene, what is the hybridization on each carbon atom?
A)sp2
B)sp3
C)sp3d
D)sp
Solution
In benzene each carbon atom is joined to three other atoms-one hydrogen and two carbons. The carbon atom in benzene lacks the number of unpaired electrons to form bonds.
Complete step by step answer:
-The formula of benzene is C6H6.It is a six carbon ring with three alternate double bonds.
-At ground state the electronic configuration of carbon is 1s22s22px12py1 -Since it lacks number of unpaired electron so it will promote one of the 2s2 electrons to jump into 2pz orbital.
-In excited state the electronic configuration of carbon will become- 1s22s12px12py12pz1.So we get 4 unpaired electrons and these electrons will participate in bond formation.
- The carbon atoms hybridize their outer orbital before forming the bonds as they have only three orbitals to hybridize. So they use 2s and two 2p orbitals to hybridize to form 3 sp2 hybrid orbitals and leave the other 2p electrons unchanged.
- The three sp2 hybrid orbitals arrange themselves at 120∘ to each other in the plane. Out of the three hybrid orbitals two orbitals overlap axially with orbitals of the neighboring carbon atoms on the both sides to form sigma bonds.
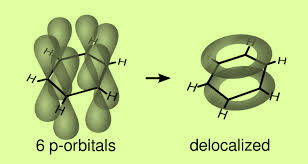
The left p orbital overlap sidewise with similar orbitals of the other carbon atoms on either side to form two sets of pi-bonds. So the resultant pi-cloud is formed over all the six carbon atoms. This is known as the delocalization of electron charge. Benzene has trigonal planar geometry.
So the correct answer is A.
Note:
Benzene has following applications-
1.It is used to make plastics, resins, synthetic fibers.
2. It is used to prepare detergents, dyes, drugs and pesticides.
