Question
Question: In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed that a ray of light incident at a...
In an experiment with a rectangular glass slab, a student observed that a ray of light incident at an angle of 55∘ with the normal on one face of the slab, after refraction strikes the opposite face of the slab before emerging out into air making an angle of 40∘ with the normal. Draw a labelled diagram to show the path of this ray. What value would you assign to the angle of refraction and angle of emergence?
Solution
This question is observation based according to the question we have drawn the figure and after labelled it. And then we will assign the value to the angle of refraction and angle of emergence.
Complete step by step solution:
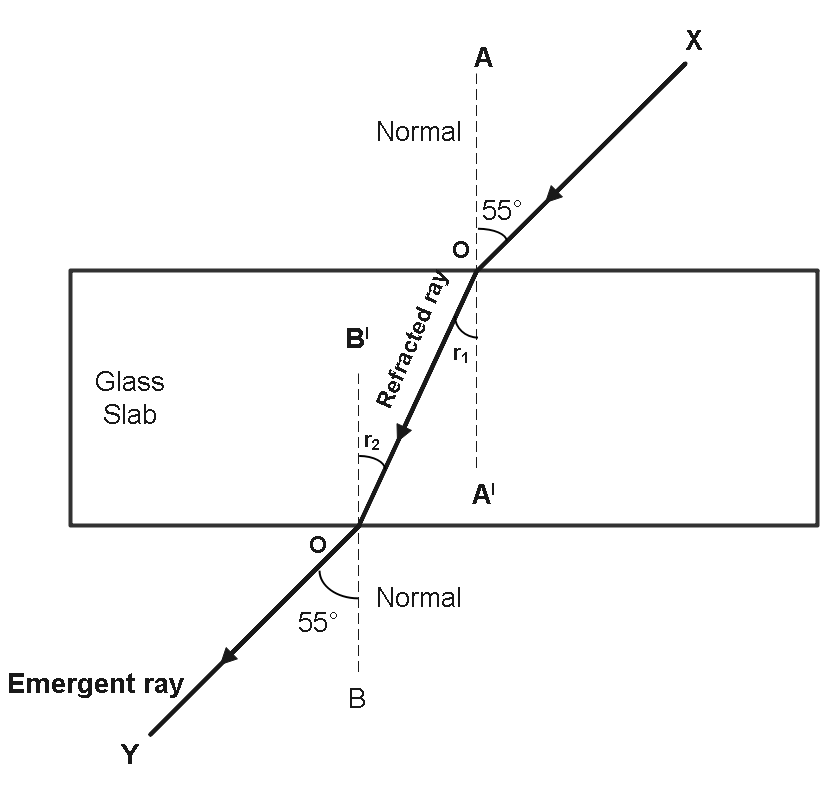
In this diagram, OX is the incident ray.
The angle of incidence for first surface, ∠i=55∘
The angle of incidence for second surface, ∠i=40∘
r1 and r2 is 40∘
So, the angle of refraction at first surface r1=40∘
As, the emergent ray is parallel to the incident ray, the angle of emergence must be equal to the angle of incidence, i.e.,
∠BOY=55∘
Hence,
The angle of refraction is, r1=40∘
And, the angle of emergence, ∠BOY=55∘ .
Note:
The incident ray, the refracted ray and the normal to the interface of two transparent media at the point of incidence, all lie in the same plane.
The ratio of sine of angle of incidence to the sine of angle of refraction is a constant, for the light of a given colour and for the given pair of media. This law is also known as Snell’s law of refraction.
