Question
Question: In a U-tube experiment, a column AB of water is balanced by a column CD of paraffin. The relative de...
In a U-tube experiment, a column AB of water is balanced by a column CD of paraffin. The relative density of paraffin is:
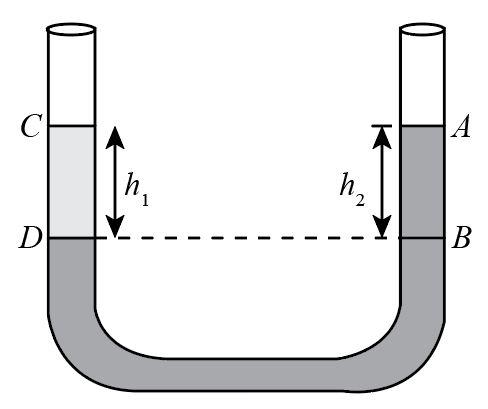
A.h1h2 B.h2h1 C.h1h2−h1 D.h1+h2h2
Solution
This question tests us of our knowledge of fluid dynamics. Here we have to use the condition of the U-tube and the condition of a balanced U-tube. And then we will use that condition to find the relative density of paraffin.
Complete step by step answer: For a balanced U-Tube the pressure in both the columns is equal. Therefore, the pressure acting due to the liquids in each column is given as:
P=P0+ρgh, where ρ is the density of the liquid, g is the acceleration due to gravity and h is the height of the liquid column and P0 is the atmospheric pressure.
Therefore, the pressure in column one is:
PCD=P0+ρpgh1
And the pressure in the second column is:
PAB=P0+ρwgh2
And for the condition of balanced U-Tube these two pressure values would be equal.
Equating the above two equations, we will get:
PAB=PCD P0+ρwgh2=P0+ρParaffingh1
Cancelling the atmospheric pressure P0 from the above expression, we get:
ρwgh2=ρParaffingh1
Now we have a relation involving the density of the paraffin, water and the heights of the water columns.
Now if we consider the formula of relative density of paraffin it is given below:
relativedensity=ρwρparaffin
Therefore, if we arrange the relation which we derived we can find the relative density of paraffin:
ρwgh2=ρParaffingh1 ρwρParaffin=gh1gh2 ρwρParaffin=h1h2 relativedensity=h1h2
Hence, the relative density is h1h2 and the correct option from the given options is (A.)
Note: In questions like these we have to apply concepts of relative quantities which is the ratio of the quantity with the standard quantity. Also, when calculating pressure in a U-tube one should always add the factor of atmospheric pressure.
