Question
Question: In a triangle ABC, G is the centroid (point of concurrency of the triangle’s medians) and E is any p...
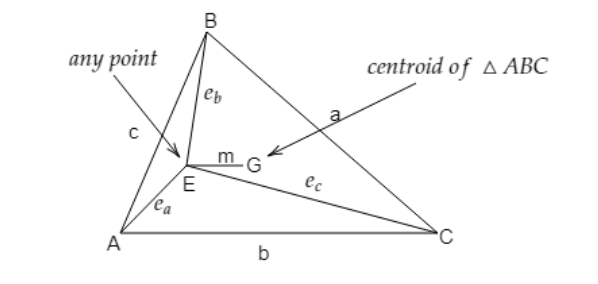
In a triangle ABC, G is the centroid (point of concurrency of the triangle’s medians) and E is any point. If BC = a , AC = b , AB = c , AE = ea , BE = eb , CE = ec and EG = m then find the value of ea2+eb2+ec2−3m2a2+b2+c2 .
Solution
Hint : The point of concurrency is a point where three or more lines or rays intersect with each other. Use triangles AEG, BEG and CEG and make an equation by keeping in mind the lengths of the sides then squaring both sides of all equations and then them all to find the value of the expression given in the question.
Complete step-by-step answer :
A centroid is a point where three medians of a triangle meet. In other words, the centroid G of a triangle ABC is the intersection of the three medians or the average of the three vertices (A, B, C).
It is given that BC = a , AC = b , AB = c , AE = ea , BE = eb , CE = ec and EG = m
As we know that if G is the centroid of a triangle and we joined the centroid of the triangle to the vertices then
GA + GB + GC = 0 --------- (i)
Also it is given that E is any point in the triangle ABC from which we connect it to the vertices of the triangle. Also the line segment EG is in the direction from E to G. Therefore, in triangle AEG we have
EA=EG + GA
On squaring both sides we get
∣EA∣2=∣EG∣2 + ∣GA∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GA∣ ------- (ii)
Similarly in triangle BEG we have
EB = EG + GB
On squaring both sides we get
∣EB∣2=∣EG∣2 + ∣GB∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GB∣ -------- (iii)
Again in the triangle CEG we have
EC = EG + GC
On squaring both sides we get
∣EC∣2=∣EG∣2 + ∣GC∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GC∣ --------(iv)
On adding equations (ii), (iii) and (iv) we get
∣EA∣2 + ∣EB∣2 + ∣EC∣2 = 3∣EG∣2 + ∣GA∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GA∣ + ∣GB∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GB∣ + ∣GC∣2 + 2∣EG∣.∣GC∣
By taking 2∣EG∣ common the above expression becomes
∣EA∣2 + ∣EB∣2 + ∣EC∣2 = 3∣EG∣2 + ∣GA∣2 + ∣GB∣2 + ∣GC∣2 + 2∣EG∣.(∣GA∣ + ∣GB∣ + ∣GC∣)
Using equation (i) we get
∣EA∣2 + ∣EB∣2 + ∣EC∣2 = 3∣EG∣2 + ∣GA∣2 + ∣GB∣2 + ∣GC∣2 + 2∣EG∣.0 ---------(v)
As we know that the centroid G of a triangle ABC is the average of the three vertices of the triangle therefore we can say that ∣AB∣2 + ∣BC∣2 + ∣CA∣2 = 3(∣GA∣2 + ∣GB∣2 + ∣GC∣2) that is 3∣AB∣2 + ∣BC∣2 + ∣CA∣2 = ∣GA∣2 + ∣GB∣2 + ∣GC∣2
So the equation (v) becomes
∣EA∣2 + ∣EB∣2 + ∣EC∣2 = 3∣EG∣2+3∣AB∣2 + ∣BC∣2 + ∣CA∣2
Now by substituting the values given in the question we get
ea2 + eb2 + ec2 = 3m2+3a2 + b2 + c2
By shifting 3m2 to the left side we have
3a2 + b2 + c2 = ea2 + eb2 + ec2−3m2
Or we can write the above expression as
ea2 + eb2 + ec2−3m2a2 + b2 + c2 = 3
Hence the value of ea2 + eb2 + ec2−3m2a2 + b2 + c2 is 3 .
So, the correct answer is “3”.
Note : The centroid divides each of the medians in the ratio 2:1 . Centroid always lies within the triangle. Substitute the values carefully otherwise you will get the wrong answer. Keep in mind all the properties of a triangle or formulas that we used in the solution. Also keep in mind that GA + GB + GC = 0 as G is the point of concurrency in the triangle ABC.
