Question
Question: In a series LCR circuit R=200 Omega and the voltage and the frequency of the main supply is 220 V an...
In a series LCR circuit R=200 Omega and the voltage and the frequency of the main supply is 220 V and 50 Hz respectively. On taking out the capacitance from the circuit the current lags behind the voltage by 30 degree. On taking out the inductor from the circuit the current leads the voltage by 30 degree. The power dissipated in the LCR circuit is:
Solution
In this question, we will use the relation between the power and voltage in a LCR circuit. Here, by substituting the given values we can get the desired power dissipated in the LCR circuit. Further, we will study the basics of LCR circuit and power as well.
Formula used:
P=zV2
Complete answer:
We know that Z=R in an LCR series in resonance.
\eqalign{& P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{z} \cr}
\eqalign{& \Rightarrow P = \dfrac{{220 \times 220}}{{200}} \cr}
\eqalign{& \therefore P = 242W \cr}
Therefore, the power dissipated in this LCR circuit is given by P having an S.I unit as watt represented by W.
Additional information:
An LCR circuit also known as resonant circuit, tuned circuit or RLC circuit is an electrical circuit.
It consists of inductor L, capacitor C and resistor as shown is in the diagram.
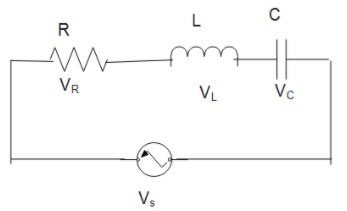
The LCR circuit analysis is understood in terms of phasors.
Resistance, Inductance, and Capacitance have very different phase relationships to each other when connected to a sinusoidal alternating supply.
A capacitor consists of two or more parallel conductive or metal plates. These plates are not connected or touching each other, but rather they are electrically separated either by air or by some form of a good insulating material like waxed paper, mica, ceramic, plastic or some form of a liquid gel as used in electrolytic capacitors. This insulating layer between capacitor’s plates is commonly called the Dielectric.
We should also know about the power. It is the amount of energy transferred or converted per unit time. In the International System or S.I Unit of power is the watt. The S.I unit of power can also be written as one joule per second. Power is a scalar quantity, which means it has only magnitude not direction.
Note:
Here, we should note that capacitance is measured in Farad, or can be said as one coulomb per volt. Capacitance is dependent on the dielectric constant as well as on the distance between the two plates. The parallel plate capacitor is the simplest form of capacitor.
