Question
Question: In a right angled triangle, the hypotenuse is \[2\sqrt 2 \] times the length of the perpendicular dr...
In a right angled triangle, the hypotenuse is 22 times the length of the perpendicular drawn from the opposite vertex on the hypotenuse then the acute angles of the triangle.
Solution
Let us name the right angles triangle as ABC, right angle situated at B. First, we consider area of triangle as half the product of two sides containing the right angle and next we consider we consider area of triangle as half the product of hypotenuse and the perpendicular drawn from the opposite vertex on the hypotenuse. From this we get two equations for the area of the triangle, we need to equate both. From the formula of hypotenuse, a2+c2=b2 we will have equations in the sides of the triangle .We simplify both and get the value of both sides. Finally, we have two sides so we divide the both to get the tangent of an appropriate side angle. From here we can find the value of acute angles of a triangle.
Complete answer:
Let us consider the value of side AB as ‘c’, BC as ‘a’, CA as ’b’.
Hypotenuse=CA=b
We consider BD to be perpendicularly drawn from the opposite vertex on the hypotenuse whose length is ‘x’, as shown in figure.
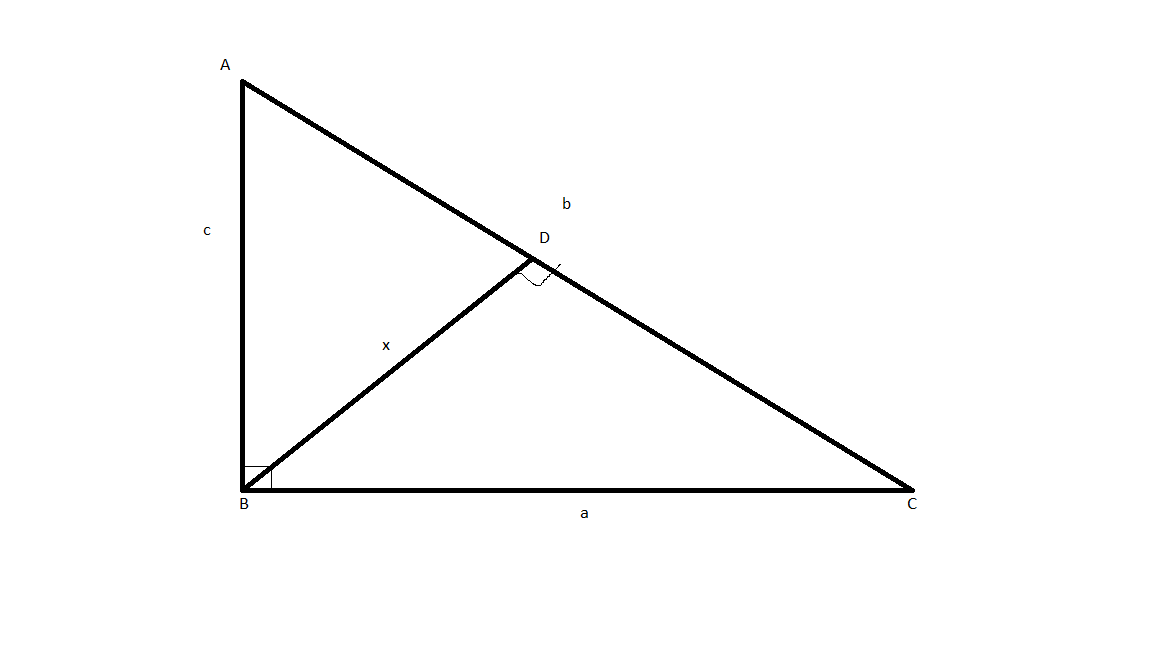
From the question, b=22×x.
Area of triangle= 21ac………….(1)
Area of triangle=21b×x
=2122x×x =222x2
Area of triangle=222x2 …………(2)
By equating (1) and (2)
By applying hypotenuse theorem,
a2+c2=b2
From (3), a=c22x2
By substituting value of ‘a’ in (4),
It is a quadratic equation in c2.
So we can use formula 2a−b±b2−4ac to find c
We take c=4x2−22x2 as if c=4x2+22x2 is taken then equation 4 is not satisfied.
For finding the value of angle ‘C’,
tanc=ac
tanC=(c22x2)c ⇒tanC=22x2c2 ⇒tanC=22x2(4x2−22x2)2 ⇒tanC=22x24x2−22x2 ⇒tanC=22x222x2(2−1) ⇒tanC=2−1
Hence,
In the triangle ABC,
A+B+C=180∘ ⇒A+C+90∘=180∘ ⇒A+C=90∘
A=90∘−22.5∘=67.5∘
So the acute angles of the right angled triangle are22.5∘,67.5∘.
Note:
In this question we use the concept of area of the triangle, that is area of triangle remains same irrespective of the side we choose in the formula. Hypotenuse side is the special condition for the right angled triangle. This condition makes the right angled triangle special and different from other triangles.
