Question
Question: In a right-angled triangle ABC, if the hypotenuse \(AB=p\) , then what \[\overrightarrow{AB}\cdot \o...
In a right-angled triangle ABC, if the hypotenuse AB=p , then what AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+CA⋅CB equals to
A. p
B. p2
C. 2p2
D. 2p2
Solution
We have to find the value of AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+CA⋅CB . From, the figure, AC⊥CB , CA⊥CB and using the rule of vectors, we will get CA⋅CB=0 . Substituting these values in AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+CA⋅CB and after some rearrangements, use the using the triangle law of vector addition (AB=AC+CB) and the property a⋅a=a2 , the required value will be obtained.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to find the value of AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+CA⋅CB .
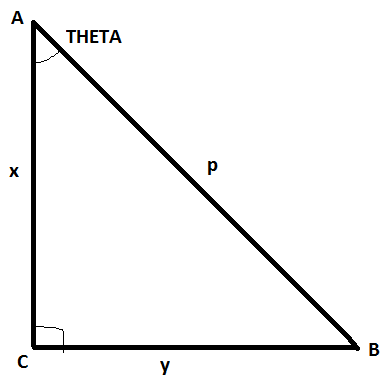
From the figure,
AC⊥CB
And CA⊥CB
We know that a⋅b=a⋅b⋅cosθ
⇒CA⋅CB=CA⋅CBcosθ
This can be written as
CA⋅CBCA⋅CB=cosθ
Given that the triangle is a right-angled triangle. Hence,
CA⋅CBCA⋅CB=cos90=0
This can be written as
CA⋅CB=0...(i)
Let us consider AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+CA⋅CB
Substituting (i) in the above equation, we will get
AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC+0
=AB⋅AC+BA⋅BC
We know that AB=−BA . So the above equation can be written as
AB⋅AC−AB⋅BC
Taking AB common, we will get
AB⋅(AC−BC)
We know that BC=−CB . So the above equation can be written as
AB⋅(AC+CB)...(ii)
Using triangle law of vector addition, that is, for a triangle shown below, A=B+C
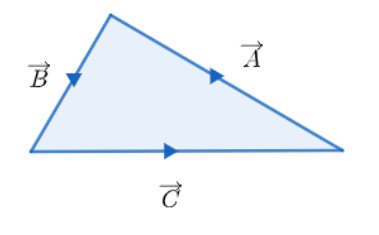
Similarly, we can express the same for the given triangle. That is,
AB=AC+CB
Hence, (ii) can be written as
AB⋅AB
We know that a⋅a=a2
Hence, AB⋅AB=AB2
=∣p∣2=p2
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: The students can make an error if they don’t know how to write the dot product of two vectors. Also, the property of vectors and triangular law of vector addition is also very important to solve this question and hence need to be very thorough in this. There can also be a chance to make error in the equation CA⋅CBCA⋅CB=cosθ by writing sinθ instead of cosθ .
