Question
Question: In a radioactive decay process \(A\) decays to \(B\) . Two graphs of the number of nuclei of \(A\) a...
In a radioactive decay process A decays to B . Two graphs of the number of nuclei of A and B versus time are given. Then choose the correct option(s)
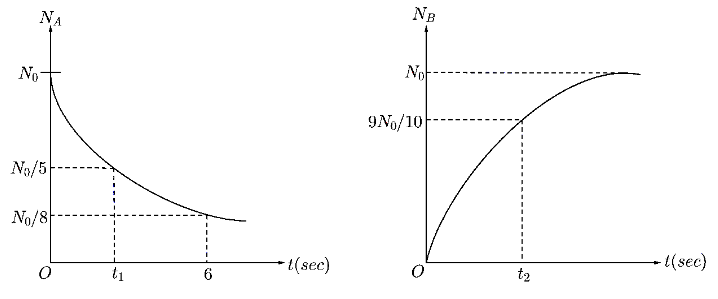
A. t2−t1=4sec
B. t2−t1=2sec
C. t1=2log25sec
D. t2=log2100sec
Solution
Complete step by step answer:
We can use the Exponential law of radioactive disintegration here as the nuclei A is disintegrated into nuclei B , which is expressed as
N=N0e−λt
Now, from the graph for nuclei A , we can obtain that at time t=6sec , the number of disintegrated nuclei is N=8N0 . Substituting this values in the equation of law of disintegration,
8N0=N0e−λ(6)
⇒81=e−λ(6)
Applying natural log on both sides,
ln(81)=lne−6λ
From the logarithmic theorems, we know ln(b1)=−lnb and lnaab=b . Applying these theorems in the above equations
−ln8=−6λ
⇒ln23=6λ
Using the logarithmic theorem lnab=blna in the above equation, we get
3ln2=6λ
⇒λ=2ln2..... (1)
Now, at time t=t1 , the number of disintegrated nuclei is N=5N0 . Substituting all the given values in Law of disintegration
5N0=N0e−λt
⇒51=e−λt
Applying natural log on both sides,
ln(51)=lne−λt
Applying logarithmic theorems,
−ln5=−2ln2t1
⇒t1=ln22ln5…… (2)
From the logarithmic theorem lnblna=lnba , the above equation can be written as
∴t1=2ln25
Now, for the disintegration curve of B , at time t=t2 , the given number of disintegrated nuclei is N=109N0
Hence, the number of disintegrated nuclei is N=N0−109N0=10N0
Substituting the values in the law of disintegration,
10N0=N0e−λt
⇒101=e−λt
Applying natural log on both sides,
∴ln(101)=lne−λt
Applying logarithmic theorems,
−ln10=−2ln2t2
∴t2=ln22ln10...…… (2)
From the logarithmic theorem lnab=blna and lnblna=lnba , the above equation can be written as
t1=ln2100
Now, taking the difference of the equation (1) and (2) ,
t2−t1=ln22ln10−ln22ln5
⇒t2−t1=ln22ln(5×2)−ln22ln5
From the logarithmic theorem ln(ab)=lna+lnb ,
t2−t1=ln22ln5+2ln2−2ln5
∴t2−t1=2sec
Hence, the correct answers are option B , C , D.
Note: Here, to avoid the use of log tables and approximation values, we have the logarithmic values as it is till the end. We can find their values from natural log tables in the initial step also. Also for the nuclei B , the graph shows the disintegrated or the number of new nuclei formed after disintegration, while the law of disintegration required the disintegrated nuclei. Hence, we must remember to take the disintegrated nuclei which can be calculated by subtracting the value from the total number of nuclei.
