Question
Question: In a p-type semiconductor majority charge carriers are _________ A. Holes B. Electrons C. Both...
In a p-type semiconductor majority charge carriers are _________
A. Holes
B. Electrons
C. Both holes and electrons
D. ions
Solution
The majority of charge carriers in p-type semiconductor depends on the doping of trivalent impurity atoms. Intrinsic semiconductors are pure semiconductors and the process of adding the atoms is termed as doping. After doping the semiconductor is known as extrinsic semiconductor.
Complete step by step solution:
Let us consider, an intrinsic (pure) semiconductor is doped with a trivalent impurity atom such as Gallium (Ga) or Boron (B). After doping the atoms form a covalent bond with the pure semiconductor atom but the bond lacks one electron for a complete outer shell of eight as shown in the below figure:-
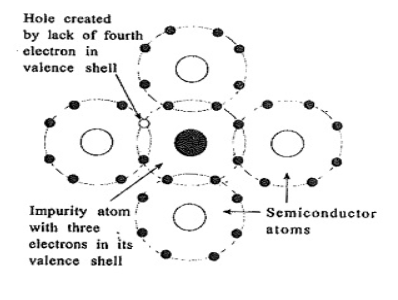
Now, as we know that the impurity atom is trivalent impurity which means it has only three valence electrons, so, extra positive charge carriers i.e., holes are created in this way in the bond with the surrounding atoms thus increasing the positive charge carriers i.e., holes.
Therefore, the answer is holes i.e., option A is correct.
Note: In case of semiconductors, the energy gap between valence and conduction band is finite. So, some electrons from the valence band, at room temperature, acquire enough energy to cross the energy gap and enter the conduction band, leaving behind a gap or vacancy with an effective positive charge, called holes. In semiconductors, the electrons and holes are called charge carriers. As ions are not produced nor considered charge carriers, so option D is incorrect.
