Question
Question: In a neutral atom \[{n_e}\] and \[{n_p}\] represent the number of electrons and protons respectively...
In a neutral atom ne and np represent the number of electrons and protons respectively. Then:
A) ne<np
B) ne=np
C) ne>np
D) None of these
Solution
There are two places where the charge is located in the atom. The nucleus contains neutrons (zero charge) and protons (positive charge). Around the nucleus, there are electrons (negative charge). The magnitude of the charge of the nucleus is equal to the magnitude of the charge of electrons. And we also know that neutrons don’t carry any charge. And from this much information, we can easily answer the question.
Complete step by step answer:
We now know that atoms are made up of 3 particles: neutrons, protons, and electrons.
Protons and neutrons are heavier than electrons and found in the nucleus at the center of the atom. Electrons are lightweight and reside in a cloud orbiting the nucleus.
Protons and neutrons have almost the same mass. However, one proton is about 1,837 times heavier than an electron. Almost every atom has an equal number of protons and electrons, and the number of protons and neutrons is the same as. Adding a proton to an atom makes a new element while adding a neutron makes an isotope, or massive version, of that atom.
Now talking about the charge,
- Electrons are negatively charged
- Protons are positively charged
- Neutrons are neutral
And if electrons and protons are equal in an atom then their magnitude of charge becomes zero because we read that charge of electrons and protons are the same in magnitude but opposite in nature.
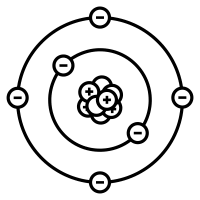
∴ The number of electrons and protons are equal in a neutral atom. Thus option B is correct.
Note:
A normal atom has a neutral charge with equal numbers of positive and negative particles. This means that an atom with a neutral charge or zero charge is one where the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number. Ions are atoms with extra electrons or deficient electrons.
Examples: Sodium, Oxygen, Nitrogen.
