Question
Question: In a condensed schematic representation of the dark reaction of photosynthesis given below, steps ar...
In a condensed schematic representation of the dark reaction of photosynthesis given below, steps are indicated by alphabets. Select the option where the alphabets are correctly identified.
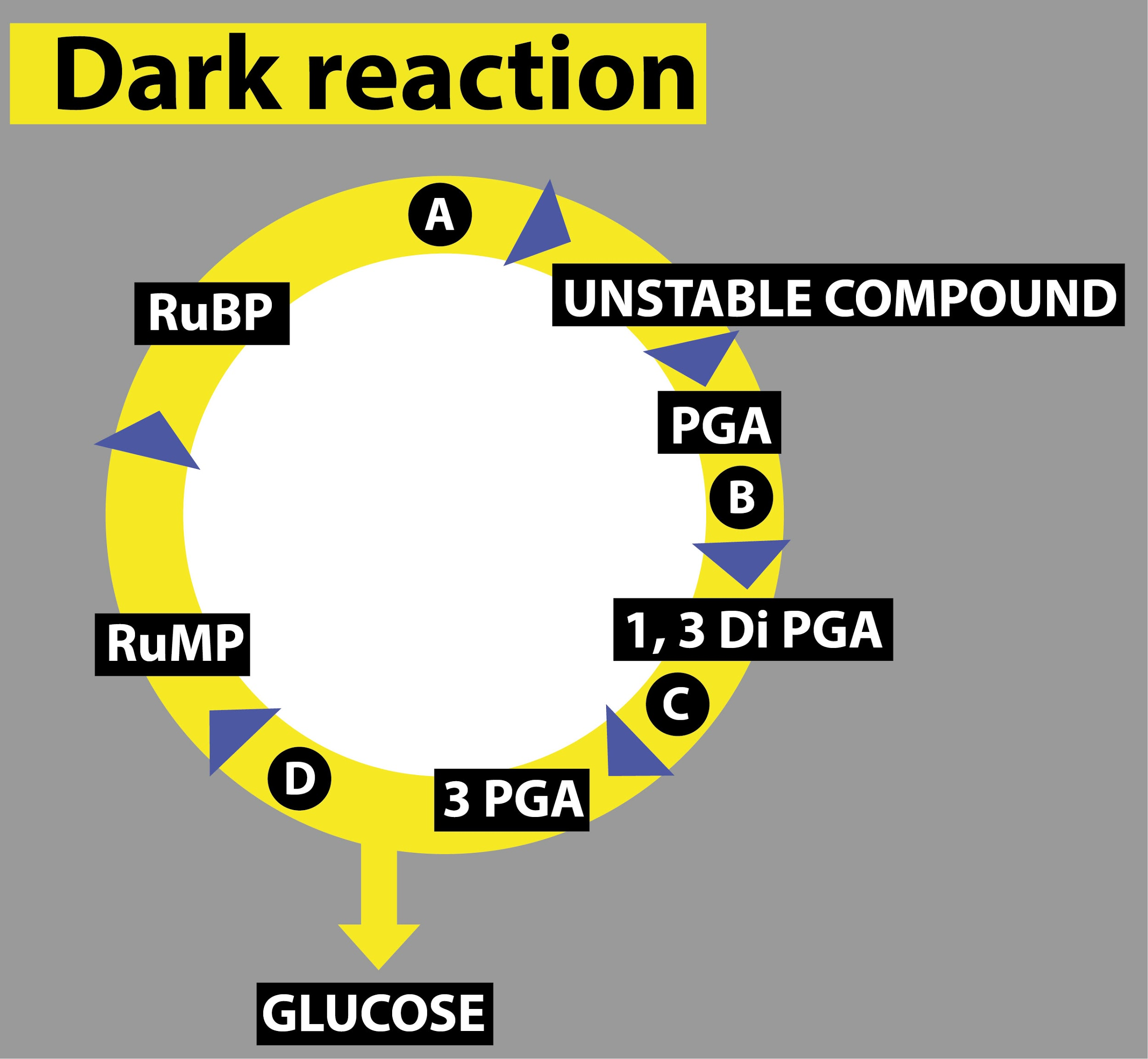
(a) A = CO2fixation, B = Reduction, C = Phosphorylation, D = Regeneration
(b) A = Regeneration, B = CO2 fixation, C = Reduction, D = Phosphorylation
(c) A =CO2fixation, B = Phosphorylation, C = Reduction, D = Regeneration
(d) A =CO2 fixation, B= Phosphorylation, C = Regeneration, D = Reduction
Solution
The addition of phosphate molecules is called phosphorylation and the Reduction of a phosphate molecule from the phosphorylated compound results in the removal of a glucose molecule and again regeneration takes place to continue the cycle.
Complete step by step answer:
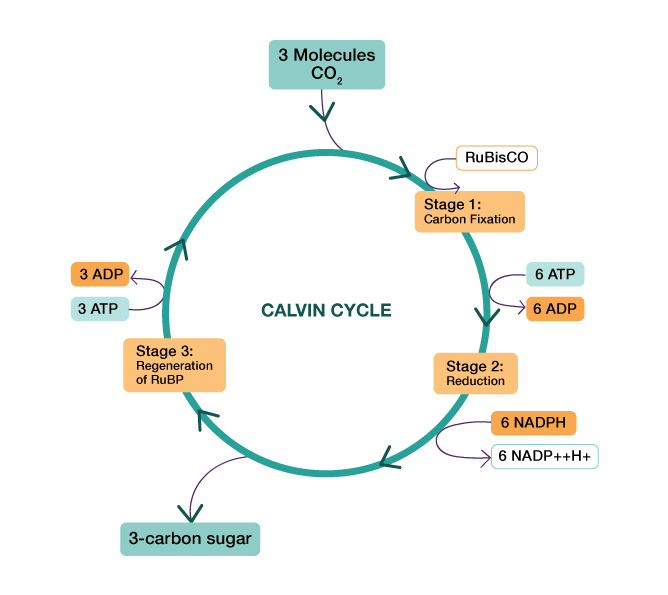
Calvin cycle is also known as the dark reaction. The first step in the Calvin cycle is carboxylation which is the fixation of carbon dioxide into a stable intermediate. Here carbon dioxide is utilized for carboxylation of RuBP results in the formation of 2 molecules of PGA. This PGA utilizes 2 ATP molecules and phosphorylates into 1,3di PGA. Now, this formed compound utilizes 2NADPH molecules for the reduction of one-carbon compound results in the removal of two molecules of triose i.e, one glucose molecule from the pathway. To continue this cyclic process RuBP should be generated. From isomers such as glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate in the presence of triphosphate isomerase with the utilization of ATP RuBP is regenerated.
So, the correct answer is ‘A = CO2 fixation, B = phosphorylation, C = reduction, D = Regeneration.
Additional information:
- The three important steps in the Calvin cycle are carboxylation, reduction, and regeneration.
- In carboxylation, RuBP undergoes carboxylation in presence of enzyme RuBisCO forms phosphoglyceric acid
- In reduction, phosphoglyceric acid in presence of enzyme phosphoglycerokinase phosphorylates into Bisphosphoglyceric acid and this is reduced into glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate in presence of an enzyme G-3-P dehydrogenase. Here 2 ATP are used for phosphorylation and 2 NADPH for reduction per one CO2 molecules fixed.
- Regeneration is the crucial step to continue the cycle uninterrupted. It requires 1 ATP for phosphorylation to form RuBP.
Note: Calvin cycle, irrespective of C3 or C4 plants it occurs in all photosynthetic plants. In this cycle, 3 molecules of ATP and 2 NADPH molecules are required for every CO2 molecule that enters the Calvin cycle.
