Question
Question: In a common emitter transistor circuit, the base current is \(40\,\mu A\), then \({V_{BE}}\) is !...
In a common emitter transistor circuit, the base current is 40μA, then VBE is
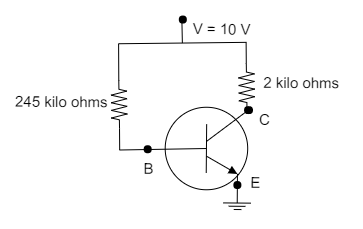
(A) 2V
(B) 0.2V
(C) 0.8V
(D) zero
Solution
Hint
When the transistor is working in the common emitter mode, then the base emitter voltage is determined by using the base bias formula of the common emitter transistor. And by using the given information the base emitter voltage is determined.
The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
⇒VCC−IBRB−VBE=0
Where, VCC is the supplied voltage to the transistor, IB is the base current, RB is the resistance of the base and VBE is the voltage in the base emitter.
Complete step by step answer
Given that, The base current is, IB=40μA
The voltage supplied to the transistor is, VCC=10V
The resistance in the base is, RB=245kΩ
The resistance in the collector is, RC=2kΩ
Now, The base bias formula of the common emitter transistor is given by,
⇒VCC−IBRB−VBE=0...................(1)
By taking the voltage of the base emitter in one side and the other terms in the other side, then the equation (1) is written as,
⇒VCC−IBRB=VBE
Now substituting the voltage supplied to the transistor, base current and resistance of the base in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
⇒10−(40×245×10−3)=VBE
Now multiplying the terms inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
⇒10−(9800×10−3)=VBE
Now moving the decimal of the term inside the bracket, then the above equation is written as,
⇒10−(9.8)=VBE
On subtracting the terms in the above equation, then the above equation is written as,
⇒VBE=0.2V
Thus, the above equation shows the voltage of the base emitter.
Hence, the option (B) is the correct answer.
Note
The common emitter type of biasing arrangement uses two resistors as a potential divider network across the supply with their centre point supplying the required Base bias voltage to the transistor. Voltage divider biasing is commonly used in the design of bipolar transistor amplifier circuits.
