Question
Question: In a circuit for finding the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a 6V battery an...
In a circuit for finding the resistance of a galvanometer by half deflection method, a 6V battery and a high resistance of 11kΩ are used. The figure of merit of the galvanometer is60μA/division. In the absence of shunt resistance, the galvanometer produces a deflection of θ=9divisions when current flows in the circuit. The value of the shunt resistance that can cause the deflection of 2θ, is closest to
A. 55Ω
B. 110Ω
C. 220Ω
D. 550Ω
Solution
From the given figure of merit we get the current passing through the galvanometer when it shows deflection of 1 division, multiplying this with θ=9 gives the current in the absence of shunt. Now find out the resistance of the galvanometer using ohm’s law. Now find out the current through the galvanometer for 2θ deflection. Now, apply the current division rule to get the value of shunt.
Formula used: Ohm’s law,
V=IR
Current division rule,
IG=IG+SS
Complete step by step answer:
We are given the figure of merit (fm)of the galvanometer as 60μA/division
Figure of merit is the measure of current passing through the galvanometer when it shows deflection of 1 division.
We are said that in the absence of shunt resistance, the galvanometer is showing a deflection of θ=9divisions
Therefore current I0 flowing through galvanometer in the absence of shunt will be,
I0=θ×fm=9×60μA/div
⇒I0=540μA ……………………… (1)
In the circuit we have a 6V battery and a high resistance of11kΩ, so from ohm’s law we have,
V=IR
But R is the total resistance of the circuit, which here is the sum of the resistance galvanometer and of high resistance.
V=I(R+G)
Where, G is the resistance of galvanometer.
Substituting the values,
6=540×10−6(11kΩ+G)
⇒G+11kΩ=11.11kΩ
⇒G=110Ω
Now we have to find the value of shunt that can cause a deflection of 2θ in the galvanometer.
For 2θ deflection, the current passing through galvanometer will be,
Ig=2θ×60=29×60=270μA
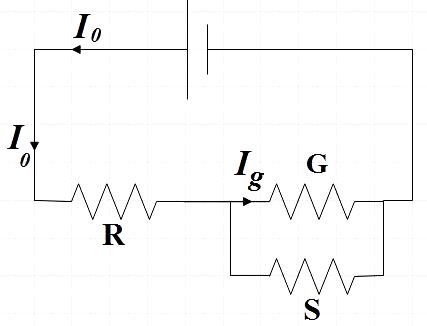
Now when we connect a shunt parallel to the galvanometer, by current division rule, we have,
Ig=I0×G+SS
⇒270μA=540μA×110Ω+SS
⇒S110+S=270540=2
⇒S=110Ω
Therefore, the value of the shunt resistance that can cause the deflection of2θ, is closest to110Ω
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: Current division is simply based on the fact that in parallel circuits the current is divided into a number of parallel paths. Parallel circuits are the ones with all components having their terminals connected together sharing the same two node ends. The current can also have different values through each component.
