Question
Question: If you are wearing wet clothes, and the water evaporates, it cools you down. How does the kinetic th...
If you are wearing wet clothes, and the water evaporates, it cools you down. How does the kinetic theory explain the cooling effect?
Solution
When water evaporates, high kinetic energy molecules escape resulting in a lowering of average kinetic energy. And kinetic theory states that average kinetic energy directly depends upon temperature. So, to completely evaporate the water molecules consumes energy from the surrounding.
Complete answer:
The evaporation of water includes phase transition of water molecules from the liquid state to the gaseous state. This transition requires energy to break the strong intermolecular hydrogen bond between water molecules.
Now, according to kinetic theory, the molecules of matter are constantly moving in all directions at random speeds. So, different molecules will have different kinetic energies.
During evaporation, only those water molecules can easily escape into the atmosphere, if they possess kinetic energy high enough to break the bonds with surrounding molecules and are present at the surface of the water.
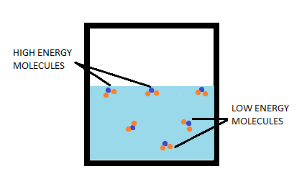
When these high kinetic energy molecules leave, the average kinetic energy of the remaining matter decreases. And according to kinetic theory, the average kinetic energy is directly proportional to the absolute temperature.
So, the temperature will also decrease. Then, the water molecules take up heat from our body to increase their kinetic energy so that they can escape and turn into vapors. This taking up of heat from our body by water molecules results in the cooling effect.
Hence, if we are wearing wet clothes, then according to kinetic theory the average kinetic energy and temperature of the water will decrease when evaporation takes place. So, they take up heat energy from our body resulting in the net cooling effect.
Additional information: The rate of evaporation depends upon many factors. It increases with an increase in surface area and temperature. The rate of evaporation also increases on a windy day.
Note: The decrease in average kinetic energy and temperature of water molecules do not result in cooling, but the consequent transfer of heat from our body to water molecules to increase their energy so that they can vaporize is the main reason behind the cooling effect that we feel.
