Question
Question: If vertices of an ellipse are \[{\text{( - 4,1),(6,1)}}\]and \[{\text{x - 2y = 2}}\]is a focal chord...
If vertices of an ellipse are ( - 4,1),(6,1)and x - 2y = 2is a focal chord, then the equation of ellipse is
A) 16(x - 1)2 + 25(y - 1)2 = 1
B) 25(x - 1)2 + 16(y - 1)2 = 1
C) 25(x - 1)2 + 9(y - 1)2 = 1
D) 9(x - 1)2 + 25(y - 1)2 = 1
Solution
Use the concept that the length of the major axis is 2a. And then the focal chord will pass through the focal point so let the focal point be (ae,0). As a is known and so calculate b, as e = 1 - a2b2 and hence from here b can be calculated. Use the general equation of ellipse which is given as a2x2 + b2y2 = 1, for centre(0,0). Thus, the equation can be obtained.
Complete step by step solution: As per the given the vertex of ellipse are ( - 4,1),(6,1) and the focal chord is given as x - 2y = 2,
Let, (x1,y1)=(6,1) and (x2,y2)=(−4,1)
Diagram:
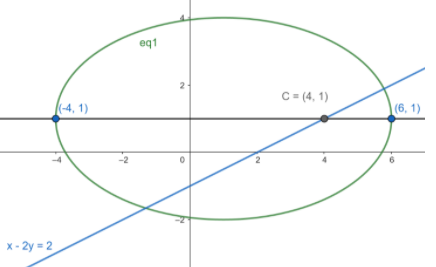
As per the diagram we can see that the length of major axis given here is 2awhich is equal to(x1−x2)=(6−(−4))=10.
So,
Here we can calculate the centre of ellipse as both the vertices are known, which are(x1,y1)=(6,1) and (x2,y2)=(−4,1)
So we use the section formula to calculate the centre of ellipse,
(2x1+x2,2y1+y2)
On substituting the values (x1,y1)=(6,1) and (x2,y2)=(−4,1) we get,
And so the focal point of the ellipse can be given as (ae,1),which will satisfy the focal chord x - 2y = 2
∴x - 2y = 2
On substituting the point (ae,1), we get,
⇒ae - 2(1) = 2
On simplification we get,
⇒ae = 4
Now as a = 5,
⇒e = 54
Hence, as we know the value of e, now calculate b using the formula e = 1 - a2b2
On substituting values of e and a we get,
⇒54 = 1 - 52b2
On squaring both the sides we get,
⇒2516 = 1 - 25b2
On rearranging we get,
⇒25b2 = 1 - 2516
On simplification we get,
⇒25b2 = 259
On further simplification of the above equation we get,
⇒b2 = 9
On taking positive square root we get,
⇒b = 3
Hence, as we know the values of a and b and centre,and the equation of ellipse is a2(x - h)2 + b2(y - k)2 = 1, where (h,k) is centre,
On substituting the values of a = 5,b = 3and centre as (1,1), we get,
Hence, option (c) is our required correct answer.
Note: You should always first draw the diagram and then proceed further to solve the question and proper calculations should be done.
An ellipse is a plane curve surrounding two focal points, such that for all points on the curve, the sum of the two distances to the focal points is a constant. As such, it generalizes a circle, which is the special type of ellipse in which the two focal points are the same.
Or
A plane curve whose sums of the distances of each point in its periphery from two fixed points, the foci, are always equal. It is a conic section formed by the intersection of a right circular cone by a plane that cuts the axis and the surface of the cone.
