Question
Question: If there are 81 million bases in RNA of human cell, then calculate the total number of introns prese...
If there are 81 million bases in RNA of human cell, then calculate the total number of introns present in cDNA
A. 27 million
B. Zero
C. Equal to ribonucleotides
D. Half the number of ribonucleotides
Solution
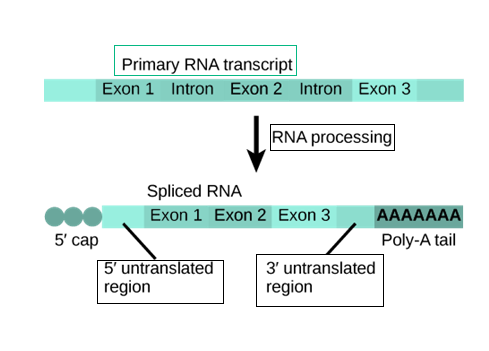
The human cell is eukaryotic. Eukaryotic genes commonly contain introns (that are essentially non-coding sequences i.e. they do not code for proteins). These are removed after mRNA is synthesized resulting in the formation of the complementary or cDNA.
Complete answer: Introns and exons are nucleotide sequences within a gene. Introns are removed by RNA by a process called splicing, as RNA matures, meaning that they're not expressed within the final messenger RNA (mRNA) product; while exons continue to be covalently bonded to one another so as to make mature mRNA. Introns are often considered as intervening sequences, and exons on the other hand are known as the expressed sequences. Introns are discarded from the pre-mRNA by the activity of a complex known as the spliceosome complex. The spliceosome is formed from proteins and little RNAs that are associated to make protein-RNA enzymes called small nuclear ribonucleoproteins or snRNPs (pronounced SNRNPS). The resulting product is what we know as the complementary DNA (cDNA) is DNA; so, cDNA is devoid of any introns.
Note: It is vital for the introns to be removed precisely, as any left-over intron nucleotides, or deletion of exon nucleotides, may end in the production of wrong or flawed protein. This may occur because the amino acids that join to form the protein structure follow the sequence of codons strictly, which contains three nucleotides.
