Question
Question: If the tangent at the point P on the circle \({x^2} + {y^2} + 6x + 6y = 2\) meets the straight line ...
If the tangent at the point P on the circle x2+y2+6x+6y=2 meets the straight line 5x−2y+6=0 at a point Q on the Y-axis, the length of PQ is-
A. 4
B. 25
C. 5
D. 25
Solution
We will find out the coordinates of the centre of the circle by comparing the given equation of the circle and the general equation of the circle. Using those coordinates, we will find out the radius of the circle.
Complete step by step answer:
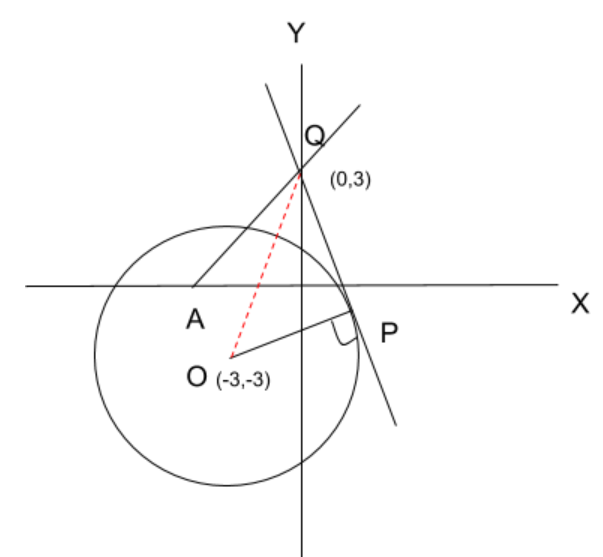
The given equation of the circle by the question is-
⇒x2+y2+6x+6y=2
The general equation of a circle is-
⇒x2+y2+2gx+2fy+c=0
Comparing both the equations, we can find out the centre of the circle-
⇒C(−g,−f)
⇒2g=6⇒3 ⇒2f=6⇒3 ⇒c=−2
Thus,
⇒C(−g,−f) ⇒C(−3,−3)
The radius of the circle-
⇒r=g2+f2−c ⇒r=32+32+2 ⇒r=9+9+2 ⇒r=25
The equation of the line given is-
⇒5x−2y+6=0 ⇒5x−2y=−6
Changing this equation into intercept form by dividing both the sides of the equation by -6, we get-
⇒6−5x+3y=1
Through this intercept form of the line, we get the coordinates of point Q (at Y axis) and the coordinates of point A (at X axis)-
⇒Q(0,3) ⇒A(−56,0)
Now, in triangle ΔOPQ, we will apply Pythagoras theorem-
⇒OQ2=OP2+PQ2
Length of OQ will we calculated by the distance formula i.e. OQ2=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2-
⇒OQ2=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2 ⇒OQ2=(0+3)2+(3+3)2 ⇒OQ2=45
Putting this value in the Pythagoras theorem applied above, we get-
OP is the radius of the circle which is 25-
⇒45=OP2+PQ2 ⇒45=(25)2+PQ2 ⇒45−20=PQ2 ⇒PQ2=25 ⇒PQ=5
Hence, the length of the tangent PQ is 5 units.
Note: Always remember to make figures in such types of questions as it makes the solution easy. Remember the general equations as they come in handy while comparing and getting the values/coordinates.
