Question
Question: If the instantaneous charge on the capacitor is \(100{\text{C}}\) and current through the circuit is...
If the instantaneous charge on the capacitor is 100C and current through the circuit is decreasing at the rate 2×103A/s then potential difference VA−VB is equal to
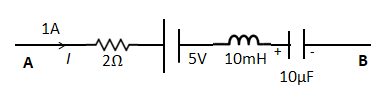
A. −3V
B. 3V
C. 37V
D. 7V
Solution
Capacitor: A capacitor is an Electrical device that stores electrical energy in an electric field. It is a two-terminal device. The effect of the capacitor is called capacitance. It is calculated in Farad (F).
The difference in the energy that the charge carrier has between the two points in a circuit is called the Potential difference. When the resistance of the wires is much smaller than the resistance of the other elements in the circuit, the potential difference drops down to zero.
LCR circuit: It is a circuit combination of inductor, capacitor and inductor.
Formula used:
VA−VB=Ri + emf + Ldtdi, here, R is the resistance of the resistor, i is the current flowing through the circuit, emf is the electromotive force of the circuit, L is the inductance of the inductor.
Complete step by step solution:
Given details from the figure we get the values of the connected components,R= 2Ω, i= 1A, emf= 5V, L=10 mH, C= 10 μ F
Using the above values and substituting in the equation we get the value of VA−VB,
VA−VB = 2×1+5+10×10−3×2×103 = 27V
The required potential difference is 27V.
Note: The capacitance of a capacitor increases with the decrease in the distance between the plates. The materials inserted between the plates of a capacitor also change the capacitance of the capacitor. The effective increase in the area of the plates in the capacitor decreases the potential difference between the plates and increases the capacitance of the capacitor.
LCR circuit is used to measure the inductive reactance of the circuit. When there is a change in the value of current flow in the circuit the induced voltage also changes.
