Question
Question: If the earth were to suddenly contract to half its present size, without any change in its mass, the...
If the earth were to suddenly contract to half its present size, without any change in its mass, the duration of the new day be
A.18 hours
B. 30 hours
C. 6 hours
D. 112 hours
Solution
We know that reduction in Earth’s size implies the reduction in its radius, so, here the radius is reduced to half. Find the moment of inertia of earth before and after contraction keeping in mind that the mass remains constant. Now, you could substitute them and the expression of angular velocities before and after contraction in the law of conservation of angular momentum and thus get the time period of one rotation of earth, that is, the duration of a day.
Formula used:
Moment of inertia of a solid sphere,
I=52MR2
Expression for angular velocity,
ω=T2π
Law of conservation of angular momentum,
I1ω1=I2ω2
Complete step-by-step answer:
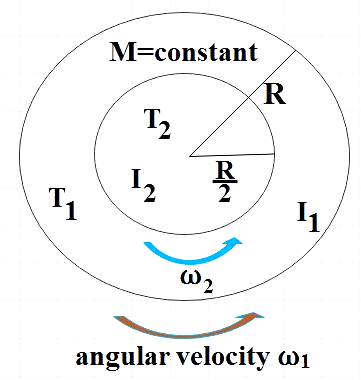
We are given that the Earth is contracted to half its present size. Change in size implies change in radius, so, here the present radius of earth (R1) is reduced by half. That is, after contraction the radius becomes,
R2=2R1 ………………………………. (1)
But during the contraction, the mass remains constant. That is,
M1=M2=M ……………………………… (2)
Due to the above mentioned contraction, the angular velocity of Earth’s rotation changes. Also, we know that angular velocity is given by,
ω=T2π
Angular velocity before contraction,
⇒ω1=T12π ………………………… (3)
Angular velocity after contraction,
⇒ω2=T22π ……………………………….. (4)
There is another quantity that is undergoing change due to contraction of earth – moment of inertia.
Moment of inertia of a solid sphere is given by,
I=52MR2
Moment of inertia before contraction,
I1=52MR12 …………………………. (5)
Moment of inertia after contraction,
I2=52MR22=52M(2R1)2=4I1 ………………………………. (6)
Now, by the law of conservation of angular momentum,
dtdL=0
⇒L=Iω= constant
⇒I1ω1=I2ω2 …………………………….. (7)
Substituting (3), (4) and (6) in (7), we get,
I1(T12π)=(4I1)(T22π)
⇒T2=4T1 ………………….. (8)
But we know the present time period rotation of our planet Earth as 24 hours. Therefore,
T1=24Hrs …………… (9)
Substituting (9) in equation (8), we get,
T2=424
⇒T2=6Hrs
Time period of rotation of Earth is what we call a day. So, for an Earth that is contracted to half its present size with mass constant, the duration of a day will be just 6hrs.
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: Though we have discussed the case where the size of the Earth is reduced by half, we could actually generalize the above relation. Let us consider that Earth is contracted to n1th of its present size,
⇒R2=nR1
⇒I2=52M(nR1)2=n2I1
Substituting in (7) and then rearranging,
T2=n2T1=n224
This generalization is under the condition that the mass of earth remains constant.
