Question
Question: If the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then the value of a cot A +...
If the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then the value of a cot A + b cot B + c cot C is equal to 25.
(a) True
(b) False
Solution
Hint:First of all, draw the diagram to visualize the question. Now, write a = 2R sin A, b = 2R sin B, c = 2R sin C and also, cotθ=sinθcosθ in the given expression. Now, proceed with solving the expression and finally substitute 4sin2Asin2Bsin2C=Rr to get the desired value.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that the circumradius and inradius of a triangle be 10 and 3 respectively, then we have to verify if a cot A + b cot B + c cot C is equal to 25 or not. Let us see what inradius and circumradius are by the diagram.
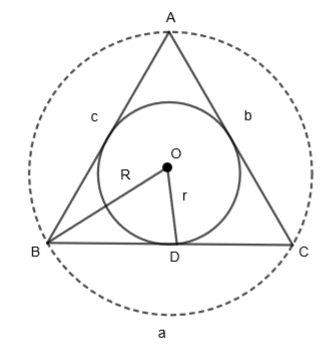
In the above figure, OB is the circumradius (R) of ΔABC and OD is the inradius (r) of ΔABC. Also, a, b and c are the sides of ΔABC. Here, we are given that R = OB = 10. Also, R = OB = OC = OA = 10 as all the radii are of the same length.
We are also given that r = OD = 3. Now, let us consider the expression given in the question.
E = a cot A + b cot B + c cot C
We know that cotθ=sinθcosθ. So by using this in the above equation, we get,
E=asinAcosA+bsinBcosB+csinCcosC
Now, we know that, a = 2R sin A, b = 2R sin B, c = 2R sin C. By substituting them in the above equation, we get,
E=2RsinAsinAcosA+2RsinBsinBcosB+2RsinCsinCcosC
By cancelling the like terms from the above equation, we get,
E=2RcosA+2RcosB+2RcosC
E=2R(cosA+cosB+cosC)
Now, we know that,
cosx+cosy=2cos(2x+y)cos(2x−y)
Also, cosx=1−2sin22x. By using this in the above equation, we get,
E=2R[2cos(2A+B)cos(2A−B)+1−2sin22C]
We know that for any triangle,
A+B+C=π
A+B=π−C
By using this, we get,
E=2R[2cos(2π−C)cos(2A−B)+1−2sin22C]
We know that,
cos(2π−θ)=sinθ
So, by using this, we get,
E=2R[2sin2Ccos(2A−B)+1−2sin22C]
We can write the above equation as,
E=2R[1+2sin2C(cos(2A−B)−sin2C)]
By replacing C by π−(A+B) in the second bracket, we get,
E=2R[1+2sin2C(cos(2A−B)−sin(2π−(2A+B)))]
We know that sin(2π−θ)=cosθ. By using this, we get,
E=2R[1+2sin2C(cos(2A−B)−cos(2A+B))]
We know that,
cosx−cosy=−2sin(2x+y)sin(2x−y)
By using this, we get,
E=2R1+2sin2C−2sin2(2A−B)+(2A+B)sin2(2A−B)−(2A+B)
E=2R[1+2sin2C(−2sin(2A)sin(2−B))]
We know that sin(−θ)=−sinθ. By using this, we get,
E=2R[1+4sin2C.sin2A.sin2B]
Now, we know that for any triangle ABC, circumradiusinradius=4sin2Asin2Bsin2C
Or, Rr=4sin2Asin2Bsin2C
By using this we get,
E=2R(1+Rr)
E=2R+2r
By substituting the values of R = 10 and r = 3. We get,
E=2(10)+2(3)
E=20+6
E=26
Hence, the value of a cot A + b cos B + c cot C = 26.
So, given the value of the expression is false.
Note: In these types of questions, students can directly remember that for a triangle ABC, (cos A + cos B + cos C) is equal to 1+Rr. This is a very useful result in the solution of the triangle and would save a lot of steps. In this question, students often make mistakes while adding angles. So, this must be avoided.
