Question
Question: If the centroid of tetrahedron OABC where A, B, C are given by (a, 2, 3), (1, b, 2) and (2, 1, c) re...
If the centroid of tetrahedron OABC where A, B, C are given by (a, 2, 3), (1, b, 2) and (2, 1, c) respectively is (1, 2, -2), then distance of P (a, b, c) from origin is
a) 195
b) 14
c) 14107
d) 13
Solution
The centroid or geometric center of a figure is the arithmetic mean position of all the points in the figure. Let ABCD is a tetrahedron whose vertices A(x1,y1,z1); B(x2,y2,z2); C(x3,y3,z3) and D(x4,y4,z4)then, the centroid (G) is given as:
G(x,y,z)=[4x1+x2+x3+x4,4y1+y2+y3+y4,4z1+z2+z3+z4]. Use this formula to find the centroid for triangle OABC and then equate the coordinates with the point (1, 2, -2) to get the values of a, b and c. Now, we get point P (a, b, c). Then, find the distance between point origin and point P (a, b, c) using distance formula:
d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2+(z2−z1)2
Complete step by step answer:
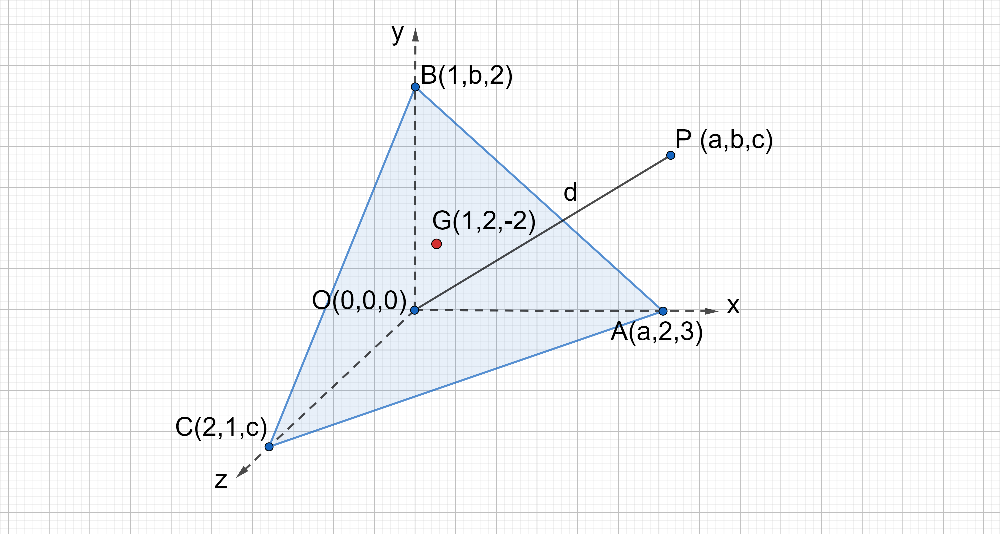
Consider the diagram of tetrahedron OABC given below, whose vertices are A(a,2,3);B(1,b,2);C(2,1,c) and O(0,0,0).
G (1, 2, -2) represents the centroid of the tetrahedron, and P (a, b, c) is the arbitrary point at a distance ‘d’ from the origin.
For a tetrahedron with vertices, A(x1,y1,z1); B(x2,y2,z2); C(x3,y3,z3) and D(x4,y4,z4), the centroid (G) is given as:
G(x,y,z)=[4x1+x2+x3+x4,4y1+y2+y3+y4,4z1+z2+z3+z4]
Therefore, for the given tetrahedron OABC whose vertices are A(a,2,3);B(1,b,2);C(2,1,c) and O(0,0,0), the centroid is
G(1,2,−2)=[4a+1+2+0,42+b+1+0,43+2+c+0]......(1)
By equating the coordinates of centroid in equation (1), we get:
