Question
Question: If \({{\text{C}}_{\text{5}}}{{\text{H}}_{{\text{11}}}}{\text{Br}} + {\text{NaCN}} \to {\text{A}}\xri...
If C5H11Br+NaCN→AH3OB+NaOHCaOC
‘C’ has the formula C5H12 which can give four structural isomeric monochloro derivatives. What is the structure of C5H11Br?
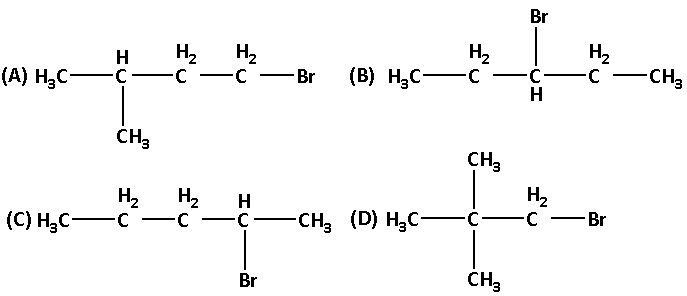
Solution
We are given a reaction sequence. The initial compound is an alkyl halide or alkyl bromide which reacts with sodium cyanide. During the reaction, the cyano groups replace the two bromine atoms. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction which produces alkyl cyanide. To solve this we have to determine the structure of initial alkyl halide.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given a reaction sequence as follows:
C5H11Br+NaCN→AH3OB+NaOHCaOC
In the reaction sequence, the initial compound is an alkyl halide or we can say alkyl bromide. The alkyl bromide reacts with sodium cyanide. This is a nucleophilic substitution reaction. During the reaction, the cyano group from sodium cyanide replaces the bromine atom of alkyl bromide. The reaction is as follows:
C5H11Br+NaCN→C5H11CN
Thus, A is alkyl cyanide C5H11CN.
The alkyl cyanide then undergoes hydrolysis and produces a carboxylic acid. Alkyl cyanide reacts with H3O+ and produces a carboxylic acid. The reaction is as follows:
C5H11CN+H3O+→C5H11COOH
Thus, B is a carboxylic acid C5H11COOH.
The carboxylic acid then reacts with sodium hydroxide in presence of calcium oxide. During this reaction first a sodium salt of carboxylic acid is formed which on reaction with calcium oxide loses carbon dioxide molecule. The reaction is as follows:
C5H11COOH+NaOH→C5H11COONaCaOC5H12
Thus, C is C5H12.
We are given that C can give four structurally isomeric monochloro derivatives. The four structural isomeric monochloro derivatives of C are as follows:
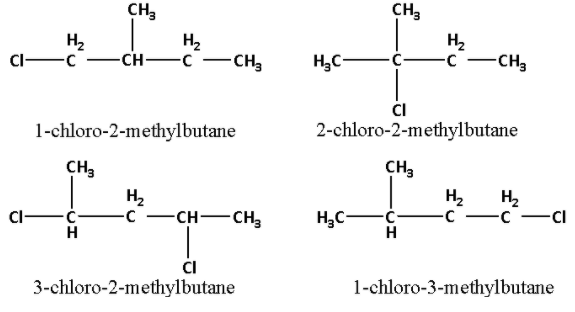
Thus, the structure of C5H12 i.e. C is as follows:
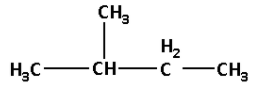
The name of compound C is 2-methyl butane.
Thus, compound A will also have the structure in which one methyl group is at carbon number 2.
Hence the correct answer is option ‘A’.
Note: The reaction in which one nucleophile is replaced by another nucleophile is known as a nucleophilic substitution reaction. The group which takes the electron pair with it and gets displaced from the carbon is known as the leaving group. The leaving group leaves as an anion or as a neutral molecule leaving behind a carbonium ion.
