Question
Question: If \[\tan (x) = \dfrac{5}{{12}}\] in the third quadrant then find other trigonometric ratios?...
If tan(x)=125 in the third quadrant then find other trigonometric ratios?
Solution
Hint : Here in this question, we have to find the value of all six trigonometric ratios i.e., sin, cos, sec, cosec and cot using a given value of tan ratio. This can be solved by using a definition of trigonometric ratios, trigonometric identities and by applying a ASTC rule of trigonometry we get the required values of all six trigonometric ratios.
Complete step-by-step answer :
Trigonometric functions are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths.
There are six trigonometric ratios, sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant and cotangent which can be abbreviated as sin, cos, tan, cosec, sec and cot.
Consider the given question:
⇒tan(x)=125 ----------(1)
given that the angle x lies in the third quadrant.
In the third quadrant, tanx and cotx are positive and all other ratios are negative.
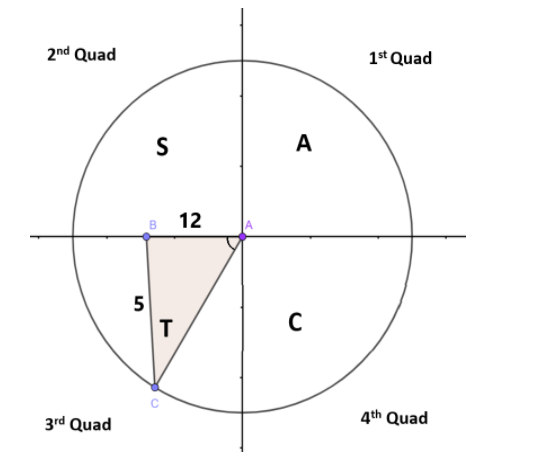
By the definition of trigonometry, Cotangent is a reciprocal of tangent ratio i.e.,
⇒cotx=tanx1
Substitute the value of tan(x) from equation (1), then
⇒cot(x)=(125)1
⇒cot(x)=512 -------(2)
Now consider, the trigonometric identity cosec2x=1+cot2x , then
⇒cosec(x)=1+cot2x
Substitute the value of cot(x) from equation (2), then
⇒cosec(x)=1+(512)2
⇒cosec(x)=1+25144
Take 25 as LCM in RHS , then
⇒cosec(x)=2525+144
⇒cosec(x)=25169
As we know 169 is a square number of 13 i.e., 169=132 and 25 is a square number of 5 i.e., 25=52 , then we have
⇒cosec(x)=52132
⇒cosec(x)=(513)2
In third quadrant cosecant are negative, then
⇒cosec(x)=−513 -------(3)
By the definition, trigonometric ratio sine is a reciprocal of cosecant i.e., sinx=cosec(x)1
substitute value of cosec(x) from equation (3), then
⇒sin(x)=(−513)1
⇒sin(x)=−135 -------(4)
Now consider, the trigonometric identity cos2x+sin2x=1 , then
⇒cos(x)=1−sin2x
Substitute the value sin(x) from equation (4), then
⇒cos(x)=1−(−135)2
⇒cos(x)=1−16925
Take 169 as LCM in RHS, then
⇒cos(x)=169169−25
⇒cos(x)=169144
As we know 169 is a square number of 13 i.e., 169=132 and 25 is a square number of 5 i.e., 144=122 , then we have
⇒cos(x)=132122
⇒cos(x)=(1312)2
In third quadrant cosine are negative, then
⇒cos(x)=−1312 -------(5)
By the definition, trigonometric ratio secant is a reciprocal of cosine i.e., sec(x)=cos(x)1
substitute value of cos(x) from equation (5), then
⇒sec(x)=(−1312)1
⇒sec(x)=−1213 -------(6)
Therefore, the values of all six trigonometric ratios are
sin(x)=−135 , cos(x)=−1312 , tan(x)=125 , sec(x)=−1213 , cosec(x)=−513 and cot(x)=512 .
Note : ASTC rule says all trigonometric functions are positive in the first quadrant (sin, cos, tan and its reciprocals). sin and cos functions are positive in the second quadrant, all other function sides are negative. tan and cot functions are positive in the third quadrant and all other functions are negative. Finally in fourth quadrant cos and sec functions are positive and all other functions are negative.
