Question
Question: If \( \tan \alpha =\dfrac{p}{q} \) , where \( \alpha =6\beta \) , \( \alpha \) being an acute angle,...
If tanα=qp , where α=6β , α being an acute angle, prove that : \dfrac{1}{2}\left\\{ p\operatorname{cosec}2\beta -q\sec 2\beta \right\\}=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}} .
Solution
To prove the above equation, first you need to convert cosec2β and sec2β into sin2β and cos2β , using the identity sinθ=cosecθ1 and cosθ=secθ1 . Then, use the identity sin2θ=2sinθcosθ and multiply numerator and denominator with p2+q2 and use triangle law of trigonometry and write sinα=p2+q2p and cosα=p2+q2q .Now, use formula sin(A−B)=sinAcosB−sinBcosA and put α=6β .
Complete step-by-step answer:
Since, we known that sinθ=cosecθ1 and cosθ=secθ1 , then we can write LHS of the above equation \dfrac{1}{2}\left\\{ p\operatorname{cosec}2\beta -q\sec 2\beta \right\\}=\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}} as:
=\dfrac{1}{2}\left\\{ \dfrac{p}{\sin 2\beta }-\dfrac{q}{\cos 2\beta } \right\\}
Take LCM of sin2β and cos2β , then we will get:
=\dfrac{1}{2}\left\\{ \dfrac{p\cos 2\beta -q\sin 2\beta }{\sin 2\beta \cos 2\beta } \right\\}
=2sin2βcos2βpcos2β−qsin2β
We know that sin2θ=2sinθcosθ , hence we will get
=sin4βpcos2β−qsin2β
Now, we will multiply numerator and denominator with p2+q2 , we will get:
=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}}{\sin 4\beta }\left\\{ \dfrac{p\cos 2\beta -q\sin 2\beta }{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}} \right\\}
Now, split p2+q2 over both the numerator term:
=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}}{\sin 4\beta }\left\\{ \dfrac{p\cos 2\beta }{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}}-\dfrac{q\sin 2\beta }{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}} \right\\}............\left( 1 \right)
Now, we will use triangle law of trigonometry (i.e. sinθ=hypotenuseperpendicular , cosθ=hypotenusebase and tanθ=baseperpendicular)
It is given in question that tanα=qp , hence perpendicular of the triangle is ‘p’ and its base is ‘q’, then, the hypotenuse will become p2+q2 , so we can draw the below diagram:
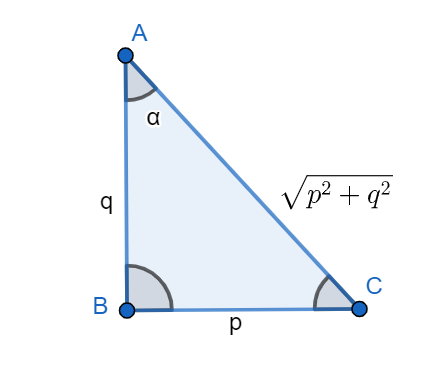
From the figure, it can be seen that we can write sinα=p2+q2p and cosα=p2+q2q .
Hence, the above equation (1) will become:
=\dfrac{\sqrt{{{p}^{2}}+{{q}^{2}}}}{\sin 4\beta }\left\\{ \sin \alpha \cos 2\beta -\cos \alpha \sin 2\beta \right\\}
Now, by using the formula sin(A−B)=sinAcosB−sinBcosA , we can rewrite the above equation as:
=sin4βp2+q2sin(α−2β)
Now, we will put α=6β in the above equation, then we will get:
=sin4βp2+q2sin(6β−2β)
=sin4βp2+q2sin(4β)
=p2+q2 = RHS
Hence, LHS = RHS
This is our required proof.
Note: Students are required to check that weather α is an acute angle or not, otherwise there is chance of change of sign while writing sinα=p2+q2p and cosα=p2+q2q , if α become greater than 90∘ .
