Question
Question: If \(R\) is the horizontal range for an inclination and \(h\) is the maximum the height reached by t...
If R is the horizontal range for an inclination and h is the maximum the height reached by the projectile, then the maximum range is given by-
(A)8hR2−2h
(B)8hR2+2gh
(C)8hR2+2h
(D)8hR2
Solution
Draw a clean diagram of projectile motion and clarify the vertical and horizontal motion of the object by dividing the initial velocity into two components.
Find the value of maximum height that the object will gain using the vertical equation of motion. Note that the final velocity in the highest point will be zero.
Use the formula of horizontal range. Note that the object will travel with a uniform velocity horizontally.
State a relation between the maximum height and maximum horizontal range. Note that the maximum horizontal range can be obtained by maximizing the sine of the angle.
Formula used:
From the equation of motion ⇒v2=u2−2gh, we get
⇒h=2gu2sin2θ , For the vertical motion the initial velocity usinθ
The horizontal distance R=ucosθ×T, the object travels with a uniform velocity ucosθ horizontally.
Where, T=g2usinθ
Rmax=gu2
Complete step by step answer:
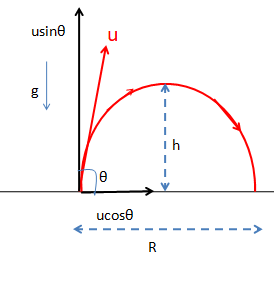
The initial velocity u has two components along vertical and horizontal.
Here, usinθ is the vertical component and also, ucosθ is the horizontal component.
For the vertical motion the initial velocity usinθ
The final velocity, v=0
Then if the maximum height be h,
Then, 0=(usinθ)2−2gh [ from the equation of motion ⇒v2=u2−2gh ]
⇒h=2gu2sin2θ..............(1)
Now the horizontal range be R
So at the time, T the object will travel the horizontal distance R
Since the object travels with a uniform velocity ucosθ horizontally and covers the distance R,
Hence, R=ucosθ×T
Where, T=g2usinθ
∴R=ucosθ×g2usinθ
⇒R=gu2sin2θ.............(2)
Now, from eq (1) and (2) we get, Rh=2sin2θsin2θ
⇒Rh=4sinθcosθsin2θ
⇒Rh=4cosθsinθ
⇒Rh=41tanθ
⇒tanθ=R4h
Now if we draw a right angle triangle by taking θ the acute angle, 4h be the perpendicular, and Rbe the base,
sinθ=16h2+R24h
Hence by putting the value of sinθ we get from eq. (1), ⇒h=gu2×2(16h2+R2)16h2..........(3)
When the value of sin2θ the highest, the horizontal range R will also be highest,
since, the highest value of sin2θ=1 , Rmax=gu2......(4)
now, from eq. (3) and (4) we get,
⇒h=Rmax×2(16h2+R2)16h2
⇒Rmax=16h22h(16h2+R2)
⇒Rmax=8h(16h2+R2)
⇒Rmax=2h+8hR2
So, the maximum range will be, ⇒Rmax=2h+8hR2
Hence, the correct answer is option (C).
Note: The locus of a projectile is given by, y=xtanθ−2u2cos2θgx2
This equation is the form of the equation of a parabola, y=ax+bx2
So, the locus of a projectile is Parabolic.
