Question
Question: If P is the point in the argand diagram corresponding to the complex number \(\sqrt 3 + i\) and if \...
If P is the point in the argand diagram corresponding to the complex number 3+i and if OPQ is an isosceles right angled triangle ,right angled at O, then Q represents the complex number:
Solution
The argand diagram is used for graphical representation of complex numbers in the form of x+iy in the complex plane. Similar to x−axis and y−axis in the two dimensional geometry we have a horizontal axis used to indicate real numbers and a vertical axis used to represent imaginary numbers in case of an argand plane. For example: 5+4i represents the ordered pair (5,4) geographically in the argand plane.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The given complex number is; P=3+i
According to the given question, let us draw the diagram to understand the question in a better way;
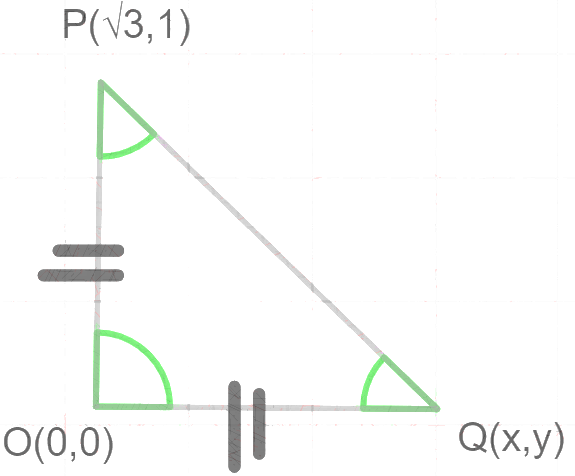
Figure (1) : Isosceles right angled triangle OPQ
⇒z=x+iy (Real part = x, Imaginary part = y)
We know that if two lines are perpendicular to each other then the product of their slopes will be equal to −1 ; i.e.
⇒m1×m2=−1
First, let us calculate the slope (m1) of line OP;
⇒m1=[3−01−0]=31 ......(1)
Now, let us calculate slope (m2) of line OQ;
⇒m2=[x−0y−0]=xy ......(2)
Put the respective values in the property m1×m2=−1 , we get;
⇒31 ×xy =−1
Simplifying the above equation;
⇒y=−3x ......(3)
Using the properties of isosceles triangles (stated in the note part) let us try to solve our question;
According to figure (1) , OP=OQ (∵Congruent sides of the isosceles triangle)
∴OP2=OQ2 will also be true.
By the distance formula between two points, we know that;
⇒d=(x2−x1)2+(y2−y1)2 ( where (x1,y1) and (x2,y2) are the coordinates of first
point and second point respectively )
⇒OP2=[((3)2−0)+((1)2−0)]
⇒OP2=3+1=4 ......(4)
Now, let us similarly find the equation for OQ;
⇒OQ2=[((x)2−0)+((y)2−0)]
⇒OQ2=x2+y2
Now, put the value of y=−3x from equation (3) in the above equation we get;
⇒OQ2=x2+(−3x)2
The above equation can be further simplified as;
⇒OQ2=x2+3x2
⇒OQ2=4x2 ......(5)
On comparing equation (4) and equation (5) , we get;
⇒4x2=4
⇒x2=1
Which means ; x=±1
Now put the value of x in equation (3) to get the value of y ; we get two cases;
When x=1 , y=−3
And x=−1 y=3
Therefore, there can be two possible values of Q , i.e. Q(±1 , ∓3)
Therefore, the answer for this question is Q=1−3i or Q=−1+3i.
Note: Here are the important properties of a right angled isosceles triangle. It will be easier to understand via a diagram, the isosceles triangle theorem states that;
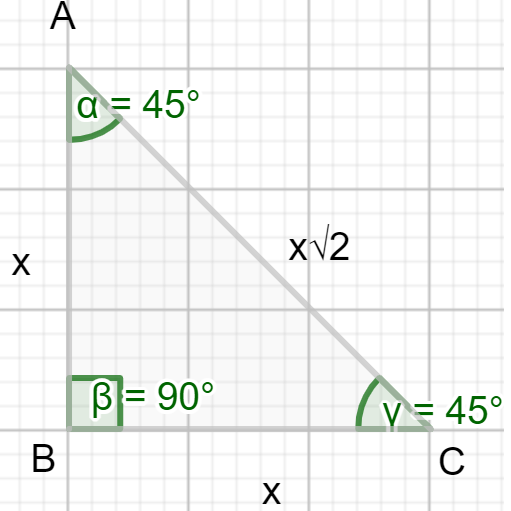
Figure (2) : Isosceles triangle theorem
(1) In the above diagram AB=BC=X , means two sides of the triangle are congruent, then the third side will be equal to X2 means the hypotenuse is 2 times the length of a leg.
(2) If AB=BC then ∠BAC=∠BCA .
