Question
Question: If one mole of the following compound is treated with \[{\text{NaOH}}\] solution, how many moles of ...
If one mole of the following compound is treated with NaOH solution, how many moles of NaOH would be required for complete neutralization.
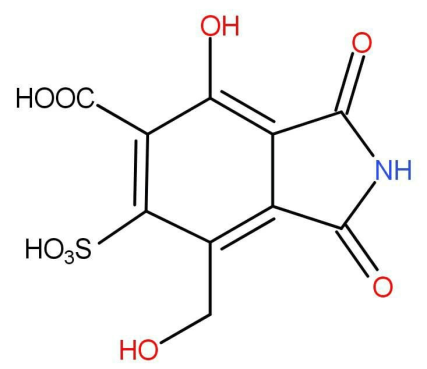
Solution
In the Presence of base, acid base reaction will occur. The acidic hydrogen present in the molecule will react with NaOH. The number of acidic hydrogen present will be equal to the number of moles of NaOH consumed.
Complete step by step answer:
Acidic hydrogen is that hydrogen which is either attached to a more electronegative atom and the negative charge formed after removal of hydrogen stabilized by resonance effect or hyperconjugation or inductive effect. If the above conditions are satisfied then the hydrogen will be called acidic hydrogen. Only acidic protons in an organic molecule react with the base to form completely neutralized products. In the above molecule given to us the acidic hydrogen as highlighted below:
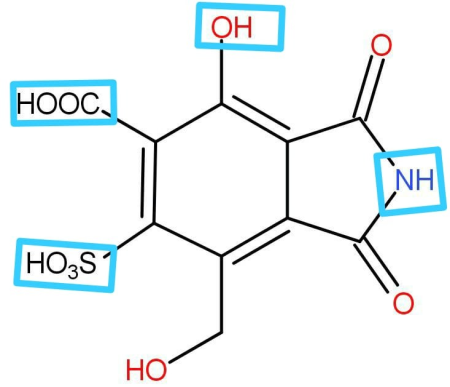
The hydrogen attached with oxygen of the hydroxide group is acidic because first of all oxygen is a more electronegative atom and the negative charge formed is stabilized by the resonance with the Pi bond that is present to alternate carbon. The next hydrogen that is acidic is the hydrogen attached with the carboxylic acid group; carboxylic acid is itself an acid. The negative charge formed in the oxygen is also in conjugation with the carbon-oxygen double bond of carboxylic acid.
Similarly the hydrogen attached to nitrogen of heterocyclic rings is also acidic because it is stabilized by the two double bonds that are present on either side of the negative charge. In the same way the hydrogen touch with the Sulphur group is also acidic hydrogen.
A total of 4 acidic hydrogens are there, so 4 moles of sodium hydroxide will be consumed for complete neutralization.
Note:
Acidic strength basically depends upon the stability of the negative charge formed and the stability of the anion formed depends on the size of atom, the electronegativity of the atom and the presence of resonance or inductive effect.
