Question
Question: If inverse trigonometric function is given as \(\cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\sin \left( {...
If inverse trigonometric function is given as \cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right)} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}. Find the value of a+b+c.
A. 3 B. 4 C. 5 D. 6
Solution
Hint: Here, we will be converting the inverse trigonometric functions into a trigonometric function next to the inverse trigonometric function so that they are just left with the angle.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Given, \cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\sin \left( {{{\cot }^{ - 1}}x} \right)} \right)} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(1)}}
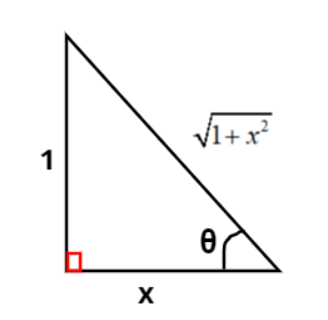
Consider θ=cot−1x⇒cotθ=x, the diagram corresponding to this function is shown in Figure 1.
Equation (1), becomes
\cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\sin \theta } \right)} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(2)}}
Here we will convert this inverse cotangent trigonometric function into inverse sine trigonometric function.
θ=cot−1x⇒cotθ=1x=PerpendicularBase
⇒Base=x and Perpendicular=1
As according to Pythagoras theorem in a right angled triangle, we can write
(Hypotenuse)2=(Perpendicular)2 + (Base)2⇒(Hypotenuse)2=12+x2⇒Hypotenuse=1+x2 As, sinθ=HypotenusePerpendicular=1+x21⇒θ=sin−1[1+x21]
Hence equation (2) becomes
\cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\sin \left( {{{\sin }^{ - 1}}\left[ {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right]} \right)} \right)} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}
We know that sin(sin−1β)=β, the above equation becomes
\Rightarrow \cos \left\\{ {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}\left( {\dfrac{1}{{\sqrt {1 + {x^2}} }}} \right)} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}{\text{ }} \to {\text{(3)}}
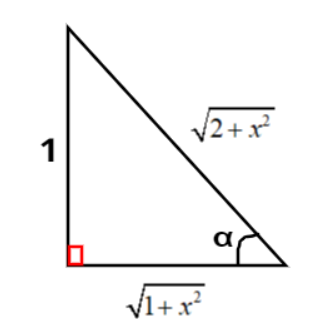
Now let tan−1(1+x21)=α⇒tanα=1+x21=BasePerpendicular, the diagram corresponding to this function is shown in Figure 2.
Equation (3) becomes,
⇒cosα=(xb+2xa+1)c1 →(4)
Here we will convert this inverse tangent trigonometric function into inverse cosine trigonometric function.
⇒Perpendicular=1 and Base=1+x2
Again according to Pythagoras theorem in a right angled triangle, we can write
(Hypotenuse)2=(Perpendicular)2 + (Base)2⇒(Hypotenuse)2=12+(1+x2)2=1+1+x2 ⇒Hypotenuse=2+x2
As, cosα=HypotenuseBase=2+x21+x2=2+x21+x2⇒α=cos−1[2+x21+x2]
Hence equation (4) becomes
\Rightarrow \cos \left\\{ {{{\cos }^{ - 1}}\left[ {\sqrt {\dfrac{{1 + {x^2}}}{{2 + {x^2}}}} } \right]} \right\\} = {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^a} + 1}}{{{x^b} + 2}}} \right)^{\dfrac{1}{c}}}
We know that cos(cos−1β)=β, the above equation becomes
⇒2+x21+x2=(xb+2xa+1)c1 ⇒(x2+2x2+1)21=(xb+2xa+1)c1 →(5)
On comparing equation (5), the values of the unknowns obtained are a=2, b=2 and c=2
Therefore, a+b+c=2+2+2=6
Hence, option D is correct.
Note: In these types of problems, conversion of trigonometric functions is required so that the next trigonometric function is eliminated with the inverse trigonometric function.
