Question
Question: If in the experiment of Wheat stone’s bridge, the positions of cells and galvanometer are interchang...
If in the experiment of Wheat stone’s bridge, the positions of cells and galvanometer are interchanged, and then balance point will
A.Change
B.Remains unchanged
C.Depend on the internal resistance of cell and resistance of galvanometer
D.None of these
Solution
The Wheat stone’s bridge consists of two branches of a parallel circuit that is joined to a galvanometer and used for identity the value of an unknown resistance in one of their branches.
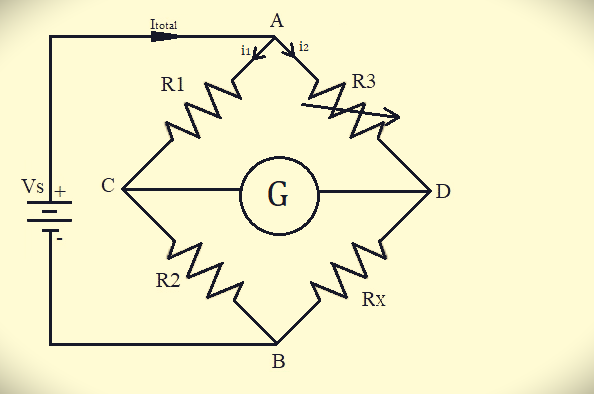
Complete answer:
The wheatstone bridge works on the principle of the ratio of their resistances that are equal to the no flow of the electric current across the circuit.
A wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit used to measure the unknown electrical resistance by balancing the two legs of the bridge circuit.
According to the above diagram the
For balanced wheat stone bridge which is
R3R1=RXR2-- (1)
If, we interchange the cell and galvanometer then the circuit becomes that are the balanced condition, R2R1=RXR3-- (2)
We can also write equation (2)
R3R1=RXR2
Thus, the balanced point remains unchanged.
So, the option (B) is correct.
Note:
A Wheat stone's bridge is more exact than the other methods to measure the resistance because the resistance is obtained using the null method and it is based on Kirchhoff's law.
The null method is used to measure the circuit is balanced to bring the pointer of the indicating instrument to zero.
In the null method, the resistance of the galvanometer and the internal resistance of the cell do not affect the null point.
In a null point method, the resistance of the galvanometer does not affect the balance point; there is no need to decide the current in resistances and the internal resistance of a galvanometer. It is the appropriate and easy method for the observer.
