Question
Question: If in a \(\Delta ABC\) ,a = 6 , b = 3 and cos ( A – B ) = \(\dfrac{4}{5}\) then find its area ?...
If in a ΔABC ,a = 6 , b = 3 and cos ( A – B ) = 54 then find its area ?
Solution
With the given details we can apply it in the formula tan(2A−B)=1+cos(A−B)1−cos(A−B)and we know that tan(2A−B)=a+ba−bcot2Cusing which we can find the value of C and since its 90 degree we can find the area using the formula 21∗base∗height.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We are given that a = 6 cm and b = 3 cm and cos ( A – B ) = 54
We know that tan(2A−B)=1+cos(A−B)1−cos(A−B)
Now applying the given value we get,
⇒tan(2A−B)=1+541−54 ⇒tan(2A−B)=55+455−4 ⇒tan(2A−B)=91=31
Using this we can substitute in the formula
⇒tan(2A−B)=a+ba−bcot2C
Substituting all the known values,
⇒31=6+36−3cot2C ⇒31=93cot2C ⇒31=31cot2C ⇒cot2C=1 ⇒2C=cot−1(1)=4π ⇒C=42π=2π
From this we get that the angle C is a right angle
Therefore the triangle ABC is a right angle triangle , right angled at B
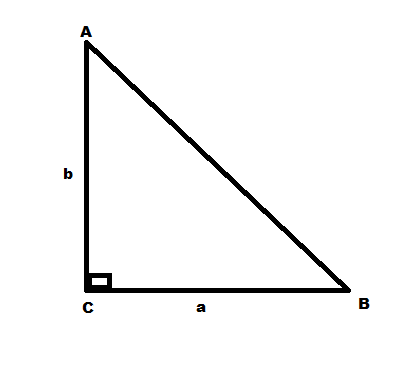
Therefore the area of the triangle = 21∗base∗height sq . units
=21∗a∗b
=21∗6∗3=21∗18=9sq.units
Therefore the area of the triangle is 9 sq.units
Note: Here we get to know that it’s a right triangle hence we use the side AC as its height but if it is not an right triangle the altitude may vary.
