Question
Question: If I is the center of a circle inscribed in a triangle ABC, then \[\left| \overrightarrow{BC} \ri...
If I is the center of a circle inscribed in a triangle ABC, then
BCIA+CAIB+ABIC is
(A) 0
(B) IA+IB+IC
(C) 3IA+IB+IC
(D) 2IA+IB+IC
Solution
Get the position of the vertices A, B, and C of ΔABC with respect to the incenter I. Use the formula for the position vector of incenter of ΔABC , BC+CA+ABBC.a+CA.b+AB.c where a , b , and c are the affixes of vertices of ΔABC and get the position vector of I. Since the calculated position vector is with respect to I so, the position vector of I with respect to I must be equal to zero. Now, solve it further and calculate the value of BCIA+CAIB+ABIC .
Complete step by step solution:
According to the question, we are given that I is the center of the circle inscribed in the triangle ABC and we are asked to find the possible value of the expression, BCIA+CAIB+ABIC .
First of all, let us assume that I is the incenter of ΔABC .
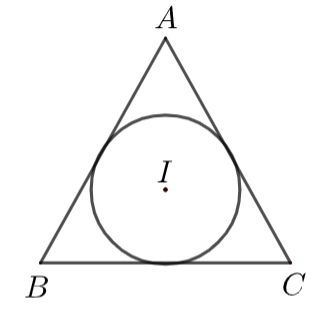
From the above diagram, we can observe that
The position vector of vertex A with respect to the incenter I = IA …………………………………………….(1)
The position vector of vertex B with respect to the incenter I = IB ……………………………………….……(2)
The position vector of vertex C with respect to the incenter I = IC …………………………………………….(3)
We know the formula for the incenter of ΔABC , BC+CA+ABBC.a+CA.b+AB.c where a , b , and c are the affixes of the vertices of ΔABC ………………………………………..(4)
Now, from equation (1), equation (2), equation (3), and equation (4), we get
The affix of the incenter of ΔABC = BC+CA+ABBCIA+CAIB+ABIC ………………………………..(5)
But the position vector of I with respect to I must be equal to zero ……………………………………..(6)
Now, from equation (5) and equation (6), we get
⇒0=BC+CA+ABBC.IA+CA.IB+AB.IC
⇒0=BC.IA+CA.IB+AB.IC ……………………………………………….(7)
BC, CA, and AB can also be written as BC , CA , and AB …………………………………………..(8)
Now, from equation (7) and equation (8), we get
⇒0=BCIA+CAIB+ABIC
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note: For this type of question, one must remember the formula for the position vector of the incenter of any triangle. That is the position vector of incenter of ΔABC , BC+CA+ABBC.a+CA.b+AB.c where a , b , and c are the affixes of vertices of ΔABC .
