Question
Question: If \(\cos \left( 2{{\sin }^{-1}}x \right)=\dfrac{1}{9}\), then find the value of x....
If cos(2sin−1x)=91, then find the value of x.
Solution
Hint: Use the fact that cos2x=1−2sin2x and hence prove that cos(2sin−1x)=1−2sin2(sin−1x). Use the fact that sin(sin−1x)=x∀x∈[−1,1] and hence prove that the given equation is equivalent to the equation 1−2x2=91 in the interval [−1,1]. Hence find the value of x in the given interval which satisfies the given equation. Verify your answer.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Before dwelling into the solution of the above question, we must understand how sin−1x is defined even when sinx is not one-one.
We know that sinx is a periodic function.
Let us draw the graph of sinx
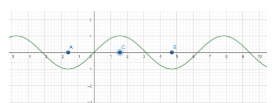
As is evident from the graph sinx is a repeated chunk of the graph of sinx within the interval [A,B] , and it attains all its possible values in the interval [A,C]. Here A=2−π,B=23π and C=2π
Hence if we consider sinx in the interval [A, C], we will lose no value attained by sinx, and at the same time, sinx will be one-one and onto.
Hence arcsinx is defined over the domain [−1,1], with codomain [2−π,2π] as in the domain [2−π,2π], sinx is one-one and Rsinx=[−1,1].
Now, we have y=sin−1x⇒x=siny
Hence, we have sin(sin−1x)=siny=x provided x in the domain [−1,1].
Now, we know that cos2x=1−2sin2x
Replace x by sin−1x, we get
cos(2sin−1x)= ˋ1−2sin2(sin−1x)
Now, we know that sin(sin−1x)=x
Hence ,we have cos(2sin−1x)=1−2x2,x∈[−1,1]
Hence, we have 1−2x2=91
Adding 2x2 on both sides, we get
2x2+91=1
Subtracting 91 on both sides, we get
2x2=98
Dividing both sides by 2, we get
x2=94⇒x=±32
Since both 32 and −32 are in the range [−1,1], we have
x=32 and x=−32 are the roots of the given equation.
Note: [1] Verification:
We have x = 32
Hence, we have cos(2sin−1x)=1−2(x)2=1−2(94)=91
Similar for x=−32, we have cos(2sin−1x)=91.
Hence our answer is verified to be correct.
[2] Graphical method:
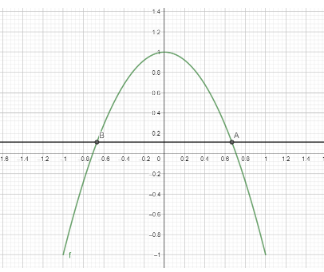
As is evident from the graph two solutions A and B exist.
