Question
Question: If \[\cos ec\left( {{{\tan }^{ - 1}}(\cos ({{\cot }^{ - 1}}(\sec ({{\sin }^{ - 1}}a))))} \right) = \...
If cosec(tan−1(cos(cot−1(sec(sin−1a)))))=p−aq , where ac[0,1].
Find the value of p+q .
Solution
We have to find the value of p+q . For this we take the left hand side of the expression. We have to solve sin−1a . We convert sin−1a into sec−1 function once we have close, we convert cot−1 function into cos−1 function. After that we convert tan−1 function into cosec−1 function. At the last we left with a value which will be free from inverse trigonometric function. Then we equate this value with the right hand side.
Complete step by step solution:
We have given that cosec(tan−1(cos(cot−1(sec(sin−1a)))))=p−aq where ac[0,1]
We have to calculate the value of p+q
L.H.S. = cosec(tan−1(cos(cot−1(sec(sin−1a)))))
We have to convert sin−1 function into sec−1 function.
Let: sec−1a=θ
a=secθ
We know that sin2θ+cos2θ=1
⇒cos2θ=1−sin2θ
⇒cosθ=1−sin2θ
Also cosθ1=1−sin2θ1
⇒ θ=sec−1(1−sin2θ1)
=secθ(1−a21)
So, L.H.S. =cosec(tan−1(cos(cot−1(sec(sin−11−a21)))))
=cosec(tan−1(cos(cot−1(1−a21))))
Now we convert cot−1 function into cos−1 function
We will to it will the help of right angle triangle.
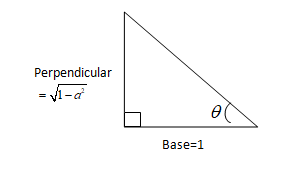
cot−1(1−a21)=θ
cotθ=1−a21
We know that cotθ=PerpendicularBase
By Pythagoras theorem
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=(Base)2+(Perpendicular)2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=(1)2+(1−a2)2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=1+1−a2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=2−a2
⇒ Hypotenuse=2−a2
Therefore value of cosθ=HypotenuseBase
⇒ cosθ=2−a21
⇒ θ=cos−1(2−a21)
So L.H.S. =cosec(tan−1(cos(cos−1(2−a21))))
=cosec(tan−1(2−a21))
Now we convert tan−1 function into cosec−1 function
Let tan−12−a21=θ
⇒ tanθ=2−a21
Also we know that tanθ=BasePerpendicular
Perpendicular =1
Base =2−a2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=(Perpendicular)2+(Base)2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=(1)2+(2−a2)2
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=1+2−a2
Here we use addition then it will become 3
⇒ (Hypotenuse)2=3−a2
⇒ Hypotenuse=3−a2
So we have cosecθ=BaseHypotenuse =13−a2
⇒ cosecθ=3−a2
⇒ θ=cosec−1(3−a2)
Therefore L.H.S. =cosec(cosec−1(3−a2))
L.H.S. =3−a2
Now we compare the left hand side with the right hand side.
⇒3−a2=p−a2
⇒3−a2=p−a2
From above we get p=3 and q=2
So value of p+q=3+2=5
p+q=5
So, the correct answer is “Option C”.
Note: In mathematics, inverse trigonometric functions are inverse of the trigonometric functions. Specifically they are inverse of sine, cosine, tangent, cotangent, secant and cosecant functions. They are used to obtain an angle from any of the angle’s trigonometric operation of the trigonometric functions.
