Question
Question: If a tangent having slope of \(-\dfrac{4}{3}\) to the ellipse \(\dfrac{{{x}^{2}}}{18}+\dfrac{{{y}^{2...
If a tangent having slope of −34 to the ellipse 18x2+32y2=1 intersects the major and minor axes in points A and B respectively, then the area of ΔOAB is equal to ( O is the centre of the ellipse)
A. 24sq.units
B. 48sq.units
C. 64sq.units
D. 24sq.units
Solution
Hint: Assume point L and use the general equation of tangent. You will get the values of a,b and m .
Put x=0 and y=0 , you will get the points as base and height. Try it.
Complete step by step answer:
Let (x1,y1) consider L(x1,y1) be a point on ellipse.
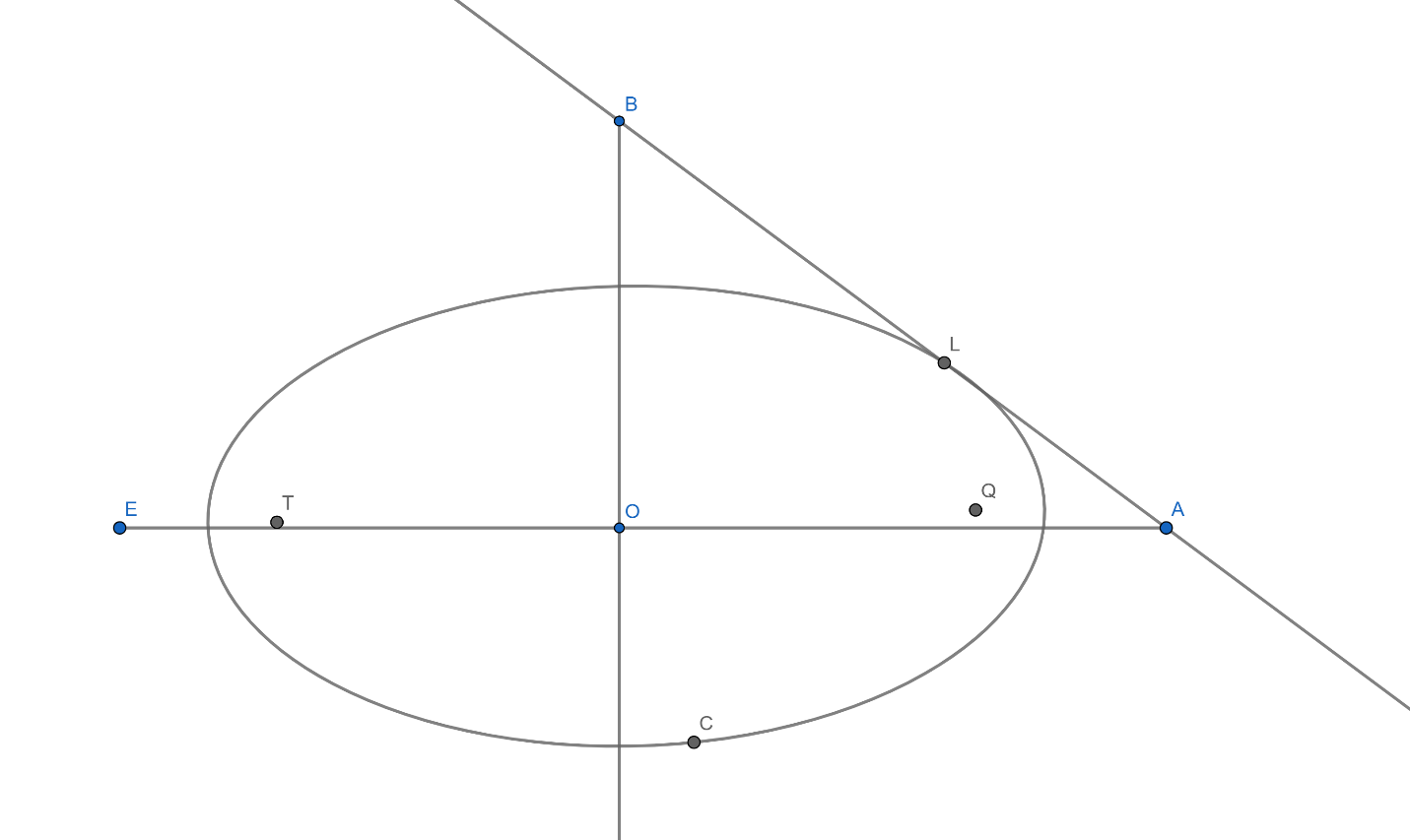
So the equation of ellipse is given as,
18x2+32y2=1………… (1)
So as the point L is on ellipse so substituting (x1,y1) in (1), we get,
18x12+32y12=1……………. (2)
So now we need the equation of tangent,
The equation of tangent to ellipse a2x2+b2y2=1 at point (x1,y1) is axx1+byy1=1 ,
So The equation of tangent at (x1,y1) is
18xx1+32yy1=1,
So for above equation of tangent at y=0 we get x− Coordinate as x118 , i.e. (x118,0) .
And at x=0 we get y− coordinate as y132 , i.e. (0,y132) .
So the equation of tangent meets the axes at A(x118,0) and B(0,y132) .
Now we have given the slope of tangent at (x1,y1) is −34 .
So −18x1×y132=−34
So now simplifying we get,
y1x1=32×34×18y1x1=86
y1x1=43
So let us write it as,
3x1=4y1
Let us say that 3x1=4y1=k .
Where k is any constant term,
So the points x1=3k and y1=4k ,
Now substituting x1 and y1 in equation (2) we get,
18(3k)2+32(4k)2=1
So simplifying we get,
189k2+3216k2=1 ………………. (Here (3)2=9 and (4)2=16 )
Now taking k2 as common we get,
k2(189+3216)=1
So now simplifying the inner bracket we get,
k2(21+21)=1k2(1)=1
So We get k2=1 ………. (3)
So we want to find area of ΔOAB ,
So we know in general the area of the triangle is equal to 21×base×height.
Area of ΔOAB =21×base×height
So in figure we can see that in ΔOAB ,
OA=base=x118OB=height=y132
So Area of ΔOAB =21×OA×OB
Area of ΔOAB =21×x118×y132
We have calculated the value of x1 and y1 ,We know that value of x1=3k and y1=4k ,
So substituting the values of x1 and y1 , we get,
Area of ΔOAB =21×3k18×4k32
Area of ΔOAB =3×4×k29×32
So simplifying it in simple manner we get,
Area of ΔOAB =4×k23×32
Area of ΔOAB =k23×8
Area of ΔOAB =k224
So we have found out the value of k2=1 , from (3)
So substituting the value of k2 in above we get,
Area of ΔOAB =1224
Area of ΔOAB =24sq.units
So we got the Area of ΔOAB as 24sq.units.
So the area of ΔOAB is 24sq.units.
Note: So in the above problem read the question carefully. So be thorough with the concept as I have considered point L so you should understand why I have considered it. So we can solve this problem by other method such as we know general equation of tangent y=mx+a2m2+b2
So a=18,b=32 and m=−34.
So substituting all values in above equation we get,
So we get final equation as,
y=−34x+8
So putting x=0 we get y−coordinate as 8 ,so A(6,0) .
And that of y=0 we get x−coordinateas 6, so B(0,8).
So here base=6and height=8
So Area of ΔOAB =21×base×height
Area of ΔOAB =21×6×8=24sq.units
So in this way you can solve it.
