Question
Question: If a straight object is at a distance \( 30cm \) and moving with uniform speed of \( 1cm{s^{ - 1}} \...
If a straight object is at a distance 30cm and moving with uniform speed of 1cms−1 towards the mirror. Then the magnitude of the speed of the image is:
(A) 1cms−1
(B) 2cms−1
(C) 3cms−1
(D) 4cms−1
Solution
In these types of questions, we must have a look at the orientation of the object. That is, if it is straight or it is inclined at an angle to the mirror. If it is a straight object, then the angle of inclination will be zero.
Formula Used: We will be using the following formula,
v=2ucosθ
Where
v is the magnitude of speed of the image
u is the magnitude of speed of the object
θ is the angle of inclination of the object to the mirror.
Complete solution Step-by-Step
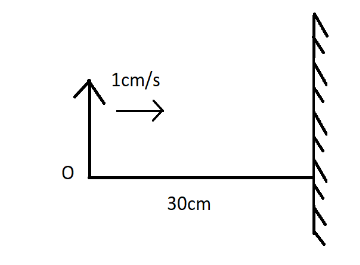
According to the question, the speed of the object is given as u=1cm/s
And the distance of the object with mirror is 30cm
Now, let us look at the formula used
We can see that the angle of inclination of the image with the mirror is 0∘
Then,
cos0∘=1
Now, we will put the known values provided in the question
So, we get
v=2ucosθ
⇒v=2×1×1
Upon solving for v , we get
∴v=2cm/s
So, the speed of the object in the mirror is calculated as 2cms−1
Hence, the correct option is (B.)
Additional Information
Different forms of image include a real image and a virtual image. The main difference between images that are real and virtual lies in the way they are produced. When rays converge, a real image is formed, whereas a virtual image occurs where rays only appear to diverge.
Note
The image of an object is the spot where, after reflecting from a mirror, light rays from that object intersect. More precisely, when, due to reflection or refraction, a beam of rays from a point source undergoes a change in direction and the refracted or reflected rays converge or appear to diverge from another point, then the second point is known as an image. Based on whether the beam of rays converge or diverge at a given point, two kinds of images are formed; real image and virtual image.
