Question
Question: If a ray of light falls along the normal of a plane mirror, then what is the angle of reflection?...
If a ray of light falls along the normal of a plane mirror, then what is the angle of reflection?
Solution
Recall the laws of reflection. The law of reflection states that when a ray of light reflects off a surface, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Make the necessary ray diagram of the reflection of the light ray of the plane mirror to support your answer.
Complete step-by-step solution:
To understand the laws of reflection, let’s draw the ray diagram of the reflection of a light ray from the plane mirror as shown in the figure below.
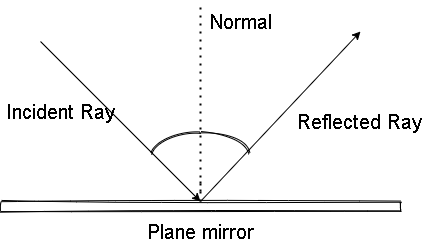
In the above diagram, the light rays which are approaching the plane mirror are known as incident rays and the ray which is leaving the plane mirror is known as a reflected ray. The line perpendicular to the mirror where the incident ray meets the plane mirror is known as normal. We always define the angle of incidence which is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal and the angle made by the reflected ray with the normal is the angle of reflection.
Now, one of the laws of reflection states that the normal line divides the incident ray and reflected ray equally from the normal. Therefore, we can say that the angle of incidence (θi) equals the angle of reflection (θr).
θi=θr
Hence, if the angle of incidence is0∘, we can say that the angle of reflection is also0∘.
Note: It is required to be sure that in actuality, there are two focal points for every lens, the same distance from the lens, on opposite sides. The distance from the lens to the focal point is called the focal length. For converging lenses, the focal length is always positive, while diverging lenses always have negative focal lengths. Plano-concave - A lens in which one side is concave and the other is Plano. Plano-concave lenses are diverging lenses.
Thus, a positive meniscus is a converging lens where one side is concave and the other convex. Negative meniscus - A diverging lens where one side is concave and the other convex.
