Question
Question: If a charge -150nC is given to a concentric spherical shell and a charge +50nC is placed at its cent...
If a charge -150nC is given to a concentric spherical shell and a charge +50nC is placed at its centre, then the charge on inner and outer surface of the shell is
A. 50nC, 100nC
B. −50nC, −100nC
C. 50nC, 200nC
D. −50nC, −200nC
Solution
As we all know that on the whole, the summation of the charges is zero. All these are related to the concept of electrostatic induction to generate static electricity. According to the concept of electrostatic induction, the positive and negative charges on either side are redistributed in such a way that the summation of the electric charges is zero.
Complete step by step solution:
Refer to the figure given below:
Draw a shell representing the charges on the center and the outer surface. Draw a figure representing the charges on the center and the shell and find the charges on the inner and outer surfaces using the concept of induction.
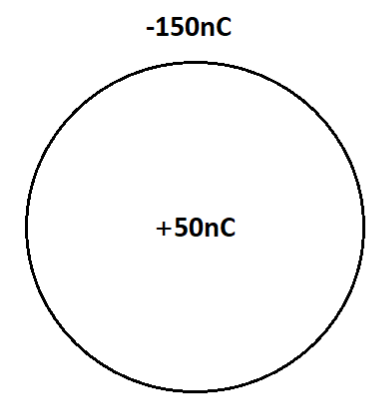
We know that when a charge is placed on a surface in an electric field, then another charge of the same magnitude is induced on the adjacent surface but with the opposite sign. This is the concept behind the Electrostatic induction of charge.
Since the charge at the center is +50nC, hence by the principle of Electrostatic induction, the charge induced at the inner surface of the shell is −50nC.
Therefore the charge induced at the inner surface of the shell is −50nC.
Hence again by the principle of induction the charge induced at the outer surface of the shell is +50nC. Therefore the net charge at the outer surface is,
−150nC+50nC=−100nC
Hence the correct option is (B).
Note:
- Static electricity is generated by bringing an electrically charged object near another object and thereby redistribution of electric charges takes place. It is most effective in the case of conducting materials.
- The only drawback of electrostatic induction is that once the charged objects are removed, the conductor loses its charge and this problem can be solved by connecting the conductor with the ground which is also known as earthing.
